Latest Blogs
By AMSAT June 30, 2025
Importance of Cybersecurity in Healthcare – Protecting Patient Safety
When you visit the doctor’s office, you trust them blindly with your personal details, your name, address, medical history, and even your insurance information. But what will happen if that sensitive information ends up in the wrong hands?
That’s where cybersecurity in healthcare comes in and why it’s highly important in healthcare more than any other industry.
This modern world is embracing the integration of technology like a new engine running a car. We are witnessing how it’s taking every industry by storm. In the healthcare industry, hospitals and clinics are increasingly bringing in digital systems to store and manage data.
With new ways of diagnosis, treatment, and health management, the importance of cybersecurity in healthcare has never been more important than today. It’s not just about protecting data anymore, it’s about protecting lives.
Now, it’s not just about accepting the latest advancements, it’s more about the vulnerabilities and threats that accompany them. So, let’s break them down together.
What is Healthcare Cybersecurity?
Healthcare cybersecurity is the application and means of ensuring protection for electronic health records, medical instruments, hospital networks, and any other electronic system or service that exists in a health environment, applying all defense mechanisms and counteractors against cyber threats.
In layman’s language, hospital and clinic security systems protect digital health data and information systems from unauthorized access or denial of service.
Types of Cybersecurity in Healthcare
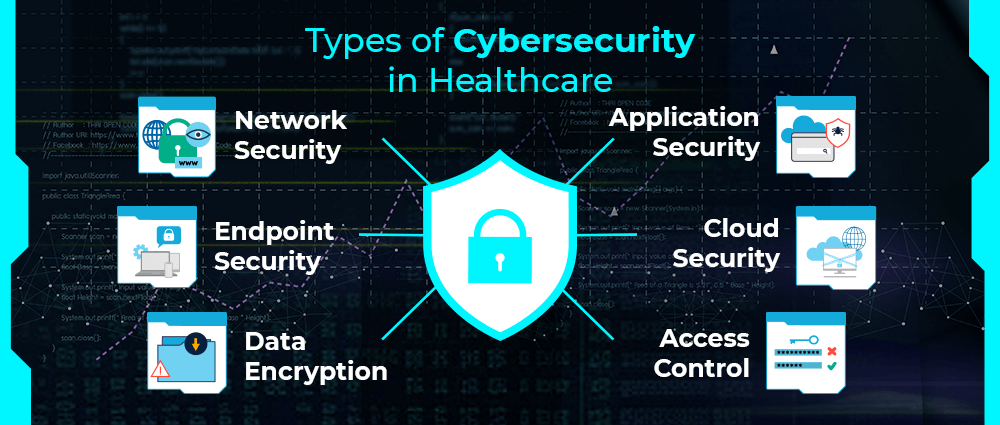
Cybersecurity in healthcare isn’t one-size-fits-all. It includes several layers of protection that work together to keep things running smoothly and safely. Let’s break them down:
Network Security
This protects a hospital’s internal network, think Wi-Fi, servers, and data transfers. Network security stops outsiders from sneaking in and messing with sensitive systems.
Application Security
Apps used for things like telehealth, prescriptions, or patient portals need protection too. This type of security ensures those apps don’t become back doors for hackers.
Endpoint Security
Every connected device, laptops, tablets, and even smart thermometers, is an entry point. Endpoint security locks those doors tight to keep threats out.
Cloud Security
Many hospitals now store data in the cloud, which makes things efficient. But it also requires solid protection from cybercriminals trying to break in from afar.
Data Encryption
Encryption scrambles sensitive data so that it’s unreadable without the right key. So even if data is stolen, it’s basically useless to the thief.
Access Control
You don’t need to give access to everyone in the hospital. This system is made to make sure that only the right people see the right data at the right time.
Each of these types plays an essential role in keeping patient data safe and hospital systems secure.
Cybersecurity in Healthcare Issues
Unfortunately, the peculiarities of the healthcare sector make daunting challenges for cybersecurity. In fact, these very weaknesses make it easy prey for the cybercriminals. Some of these cybersecurity threats comprise of:
Obsolete systems
A lot of hospitals are still using outdated and unsupported software. Such legacy systems naturally become sweet targets for hackers keen to exploit known weaknesses.
Lack of Awareness
Many healthcare workers aren’t trained in spotting cyber threats like phishing emails. One accidental click can open the door to a full-blown data breach.
Budget Constraints
Advanced cybersecurity tools and skilled IT staff can be expensive. Smaller clinics and underfunded hospitals often can’t afford top-tier protection.
High-Value Data
Patient records are like gold to cybercriminals, more valuable than credit card info. They contain names, birthdates, Social Security numbers, and insurance details.
These ongoing issues make healthcare one of the most vulnerable and frequently targeted sectors. Without the right protection, both patient data and lives can be at serious risk.
The Consequences of Cyberattacks on Healthcare
When a hospital suffers a cyberattack, it’s not just an IT problem, it’s a patient safety problem. Here’s where things get really serious, cyberattacks can do damage, some of them are:
- Delay emergency care by shutting down systems.
- Expose personal data, leading to identity theft.
- Tamper with lab results or prescriptions.
- Disrupt life-saving equipment like ventilators and infusion pumps.
In 2020, a ransomware attack in Germany caused the first death linked to a hospital cyberattack. This shows just how real and dangerous the consequences can be.
Benefits of Healthcare Cybersecurity
So why invest in cybersecurity? The benefits are huge:
Ensure Patient Safety
The significant impact of cyber security in assuring patient safety is the single most crucial area in which it plays a role. When systems are secure, doctors can get accurate, up-to-date information when making life-saving decisions. There would be no risk of tampering or going offline at important moments.
Maintains Trust Between Patients and Providers
Patients tell providers secrets about their bodies. That trust remains intact as long as the records are locked tight. One breach of trust would cause havoc and ruin a provider’s name for a decade.
Ensures Compliance with Privacy Laws like HIPAA
Regulations such as HIPAA are not really mere regulations; these are made in order to protect the privacy of the patients. The organization is made compliant by the cybersecurity in terms of proper data handling and access control. Violation of these regulations can incur huge fines as well as lawsuits.
Reduces Costs by Preventing Data Breaches
It is very expensive to recover from a cyberattack that is, really very expensive starting from ransom payment to damage repair and revenue loss. Strong cybersecurity means a wise investment that prevents these disasters from happening in the first place.
Improves Operational Efficiency
When systems are protected and streamlined, such systems enable productive work without interference. It reduces the downtime, lessens the incidence of emergencies in IT matters, fast access to critical information, better patient care, and stress-free living for people.
In short, investing in healthcare cybersecurity doesn’t just protect information, it helps keep patients safe, builds trust, and makes the whole healthcare experience more efficient and secure.
Cybersecurity Strategies and Regulations in Healthcare
Thankfully, there are strategies and regulations in place to help healthcare organizations stay secure:
Key Strategies:
- Regular risk assessments
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Employee training
- Data backups
- Incident response plans
Important Regulations:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Requires healthcare providers to protect patient data.
- HITECH Act: Strengthens HIPAA by promoting the secure use of electronic health records.
- GDPR (for Europe-based healthcare data): Protects the personal data of European citizens.
These strategies and regulations guide healthcare organizations in developing strong cybersecurity practices.
Best Practices for Healthcare Cybersecurity
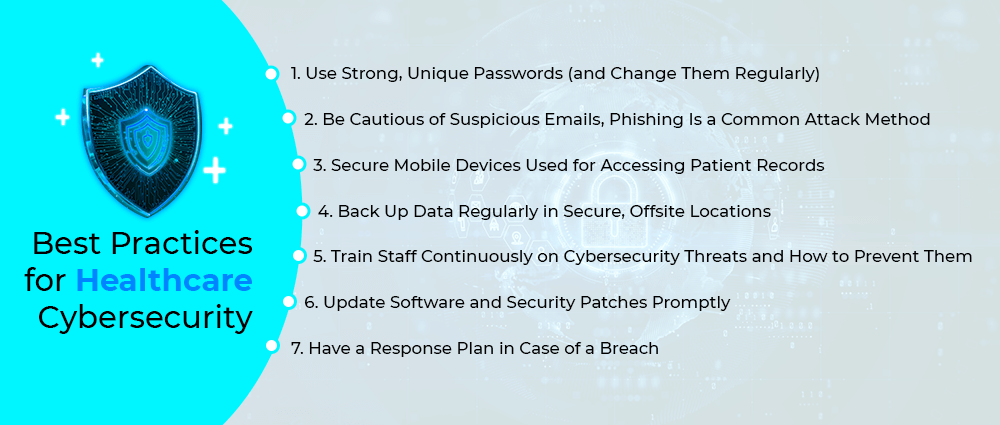
Want to keep healthcare data safe? These best practices help:
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords (and Change Them Regularly)
Weak or reused passwords are like handing hackers the keys to the kingdom. Your healthcare staff should use long, complex passwords that are different for every system, and just as importantly, they should make it a habit to change them regularly to reduce risk.
2. Be Cautious of Suspicious Emails, Phishing Is a Common Attack Method
Phishing emails are designed to trick people into clicking malicious links or sharing sensitive info. In order to keep everyone, you should train your staff to think twice before opening attachments or responding to unexpected emails. If something looks off, it probably is, better safe than sorry.
3. Secure Mobile Devices Used for Accessing Patient Records
Phones, tablets, and laptops are convenient, but also vulnerable if not properly protected. Devices used to access patient data should have encryption, password protection, and remote wipe features. This way, losing a phone won’t mean losing confidential patient info.
4. Back Up Data Regularly in Secure, Offsite Locations
Ransomware may lock you away from your data. Backups are the only escape route. Data backup on a daily basis offers you an opportunity to secure your data in an off-site location so that you are never completely at the mercy of attackers. This simple step could avert a lot of trouble for you.
5. Train Staff Continuously on Cybersecurity Threats and How to Prevent Them
No security mechanism can work if there was human error, and if those humans are not adequately trained. Cybersecurity tuition keeps common now and relevant to their problem. It endows employees in a facility with being the first line of defense rather than the weakest link.
6. Update Software and Security Patches Promptly
Old software is one of the easiest ways in for hackers. If you regularly update and secure patches, it enables you to close those gaps before they’re exploited. Make sure every system, app, and device is always running on the latest version.
7. Have a Response Plan in Case of a Breach
No system is perfect, breaches can still happen. If you have a well-prepared incident response system in place, it ensures quick action to limit damage and recover operations faster. Everyone in your company should know their role and the steps to take if something goes wrong.
Final Thoughts
In today’s digital world, the importance of cybersecurity in healthcare can’t be overstated. It’s not just about protecting data, it’s about saving lives. As cyber threats continue to grow, so does the need for strong, smart, and proactive cybersecurity strategies.
So, whether you’re a healthcare worker, patient, or IT professional, remember: protecting healthcare from cyber threats is a team effort, and it starts with awareness.
If you’re looking at ways to protect your systems, then contact the CIOs and ISOs at Amsat and get the best advice and solutions against any cyber threats that could cause your patients or their data harm.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of cybersecurity in healthcare?
The role of cybersecurity in healthcare is to protect patient data, ensure the safe operation of digital systems, and prevent disruptions that could affect patient care. It’s essential for both data privacy and patient safety.
Why is healthcare a top target for cybersecurity threats?
There are a number of reasons why healthcare is a prime target for cyber attacks, here a re few of them:
- Medical data is extremely valuable on the black market.
- Many hospitals use outdated or vulnerable systems.
- The pressure to restore systems quickly often leads hospitals to pay ransoms.
Hackers know that time-sensitive care creates urgency, and that gives them leverage to find out whatever they want and use it with malicious intent.
What Is Healthcare Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity in healthcare simply means protecting the digital health system and patient data from every possible cyber attack like hacking, ransomware, or data breach. Cybersecurity measures include a combination of technology, policy, and training to protect the patients and secure the entire healthcare system.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SOC
- Managed SOC
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.