Latest Blogs

By AMSAT Mar 16, 2024
Integrate SOAR with SIEM for Automated Threat Response
In today’s fast-evolving threat landscape, security teams are constantly bombarded with a volley of alerts. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems are built to sift through these alerts and detect potential security incidents. But there’s a catch: It’s even challenging for SIEM to keep up with the rising volume and complexity of threats. So, how to solve this conundrum? The answer lies in implementing Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR), which offers a powerful solution for automated threat response.
What is SOAR in Cybersecurity?
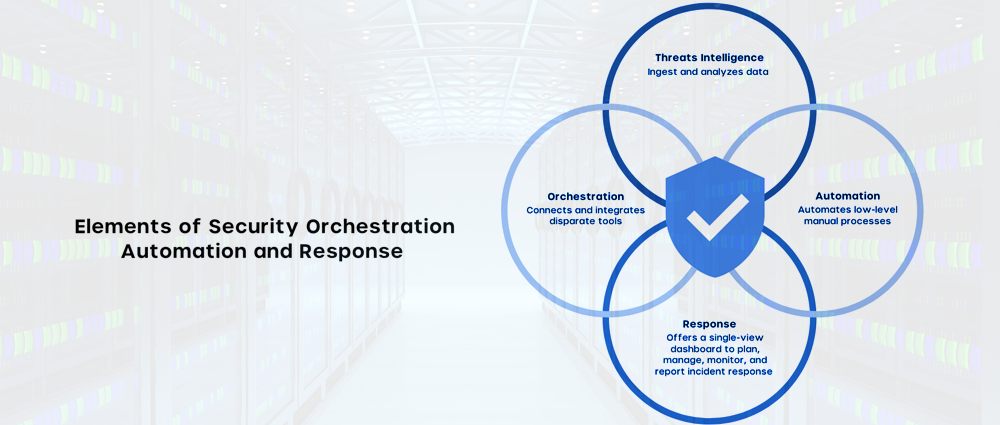
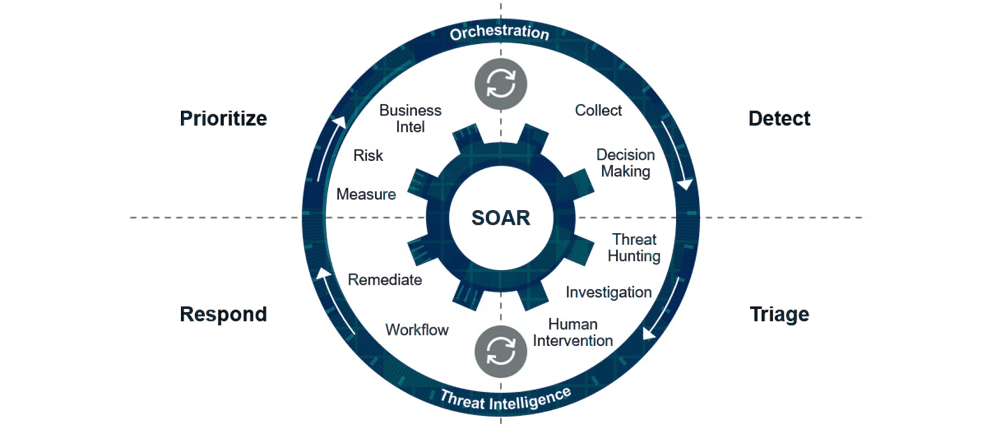
Short for Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response, SOAR is a platform that integrates various security tools and automates repetitive tasks within an incident response workflow.
Here’s a breakdown of its functionalities:
- Security Orchestration: SOAR streamlines workflows by coordinating actions across different security tools, eliminating the need for manual switching between tools and saving analysts valuable time.
- Automation: SOAR automates repetitive tasks such as data enrichment, investigation steps, and containment procedures, allowing analysts to focus on complex investigations and decision-making.
- Response: SOAR facilitates a faster and more consistent response to security incidents. By automating initial steps and providing analysts with relevant context, SOAR empowers teams to respond swiftly and effectively.
Benefits of SIEM with SOAR Integration
Integrating SIEM and SOAR ensures a powerful combination that massively improves your security posture. Here’s how:
- Faster Threat Detection and Response: SIEM excels at collecting and analyzing security data to detect potential threats. When integrated with SOAR, these alerts trigger automated workflows, accelerating investigation and containment. This translates to a reduced Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) for security incidents.
- Reduced Analyst Workload: SOAR can automate manual tasks, such as data gathering and preliminary investigation steps, freeing up experts’ time to focus on higher-level analysis, threat hunting, and incident resolution.
- Improved Incident Response Consistency: SOAR automates predefined workflows for different incident types, ensuring a steady and repeatable response approach. This minimizes human error and ensures all incidents are addressed effectively.
- Enhanced Security Visibility: SIEM and SOAR work together to provide a comprehensive view of your security environment. By correlating data from various sources, the integrated system offers a deeper understanding of threats and potential attack vectors.
- Streamlined Security Operations: Integrating SIEM and SOAR leads to a more streamlined security operation. Automated workflows and centralized management of alerts improve overall efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Integrate SIEM with SOAR Platforms
The specific steps for integrating SIEM and SOAR will vary depending on the chosen platforms. However, here’s a general framework to follow:
Planning and Analysis:
- Define your goals for integration. What specific security challenges are you trying to address?
- Analyze your existing security infrastructure: SIEM capabilities, SOAR features, and other security tools you use.
- Identify data flows and communication protocols between SIEM and SOAR.
Implementation:
- Configure SIEM to collect and analyze relevant security data. Establish log sources, correlation rules, and alerts for potential incidents.
- Configure SOAR workflows for incident response, automation, and integration with other security tools.
- Establish secure communication channels between SIEM and SOAR to ensure seamless data exchange.
Testing and Validation:
- Thorough testing of the integration is crucial. Simulate various security scenarios and validate automated workflows.
- Ensure proper logging and auditing mechanisms are in place to monitor the integrated system’s performance.
Best Practices for SIEM with SOAR Integration
- Start with Clear Goals: Establish specific objectives for the integration to guide configuration and measure success.
- Standardize Data Format: Ensure consistent data format across SIEM and SOAR for seamless data exchange and accurate analysis.
- Prioritize High-Value Alerts: Configure SIEM to prioritize alerts that require SOAR automation to minimize unnecessary workflows.
- Maintain User Roles and Permissions: Define clear roles and permission access within SIEM and SOAR for optimal security and control.
- Invest in Training: Train security analysts on using the integrated platform effectively.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Continuously monitor the performance of the integrated system and make adjustments as needed based on new threats and security requirements.
Conclusion
Integration of SIEM and SOAR can help organizations achieve a major leap forward in their security posture. Faster threat detection, automated response workflows, and improved analyst efficiency all contribute to a more secure and resilient IT environment. Nevertheless, proper planning, implementation, and best practices are key to unlocking the full potential of this powerful combination.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SIEM
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.