Latest Blogs

By AMSAT Mar 12, 2024
Advanced Threat Hunting Strategies using SIEM Analytics
In today’s dynamic cyber threat landscape, traditional security solutions often fall short in detecting sophisticated attacks. Cybercriminals constantly adapt their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to bypass signature-based defenses. This is where cyber threat hunting comes in.
Threat hunting is a proactive approach to exposing hidden threats within an organization’s network. It involves using a combination of human expertise and security tools to actively search for malicious activity. SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) plays a crucial role in threat hunting SIEM by centralizing and analyzing security data from various sources, providing valuable insights for threat hunters.
Why use SIEM for Threat Hunting?
SIEMs offer several advantages for threat hunting:
- Centralized Data Collection: SIEMs aggregate logs and events from diverse security tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and endpoints, providing a single pane of glass for data analysis. This eliminates the need for manual data collection from disparate sources, saving time and effort.
- Data Normalization: SIEMs normalize log data into a consistent format, allowing threat hunters to easily analyze and compare data from various sources even if they have different formats and structures.

- Advanced Analytics: SIEMs offer advanced analytics capabilities, including filtering, correlation, and aggregation, allowing threat hunters to identify anomalies and patterns that might indicate malicious activity.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: SIEMs can integrate with threat intelligence feeds, which provide information on known indicators of compromise (IoCs) and attacker TTPs. This helps threat hunters focus their efforts on high-risk activities and potential threats.
Advanced Threat Hunting Strategies with SIEM Analytics
Here are some advanced threat hunting strategies that leverage SIEM analytics:
- Hypothesis-Driven Hunting: This involves formulating specific hypotheses about potential threats based on industry trends, intelligence reports, or internal risk assessments. Threat hunters then use SIEM queries and analytics to search for evidence supporting or refuting their hypotheses. For example, a hypothesis might be: “Employees in the finance department are at a higher risk of spear phishing attacks.” The threat hunter can then use SIEM queries to analyze email logs and identify suspicious activity related to the finance department.
- Behavioral Analysis: SIEMs can be used to analyze user behavior patterns and identify deviations from the norm. Unusual activity like excessive login attempts, unauthorized access to sensitive data, or lateral movement within the network might indicate a potential compromise.
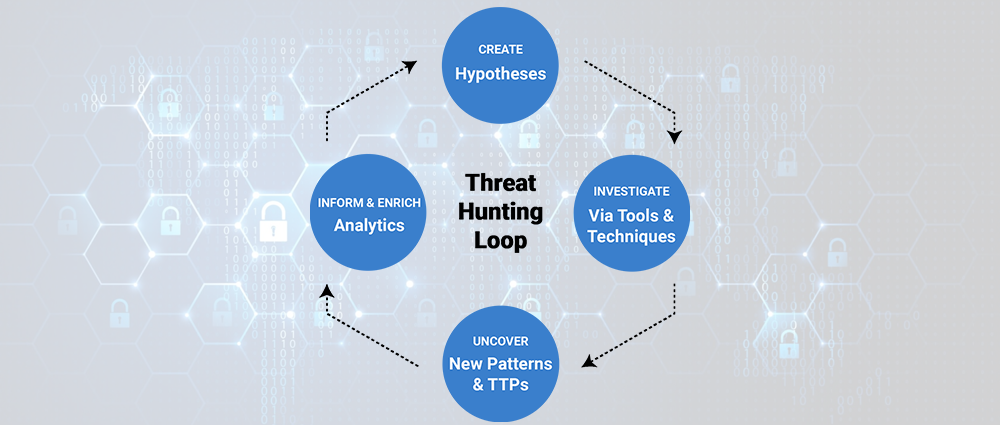
- Hunting for Unknown Threats: SIEMs can be utilized to identify unknown threats that haven’t been detected by traditional security solutions. This involves analyzing log data for anomalies such as:
- Unusual file transfers
- Unauthorized access attempts
- Unexpected network traffic patterns
- High-risk system activities
- Using the MITRE ATT&CK Framework: This framework categorizes attacker TTPs into various tactics and techniques. By leveraging SIEM analytics and searching for specific elements of the ATT&CK framework within log data, threat hunters can identify potential attack stages and investigate further.
Combining SIEM with Other Threat Hunting Tools
While SIEM is a powerful tool for threat hunting, it’s important to remember that it’s not a standalone solution. Threat hunters often utilize additional tools in conjunction with SIEM to gain a more comprehensive view of the security landscape. Some of these tools include:
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Provides real-time visibility and control over endpoints within the network.
- Network Traffic Analysis (NTA): Analyzes network traffic to identify malicious activities like malware communication and suspicious data exfiltration.
- User Entity and Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Analyzes user and entity behavior to identify potential insider threats or compromised accounts.
Automating Threat Hunting with SIEM
While there’s no substitute for human expertise in threat hunting, automated threat hunting can be a valuable tool to streamline the process and reduce the burden on security analysts. SIEMs can be configured to generate alerts based on pre-defined rules and indicators. These alerts can then be reviewed and investigated by analysts, allowing them to focus on high-priority incidents.

Conclusion
By adopting cutting-edge threat hunting strategies using SIEM analytics, organizations can significantly improve their ability to detect and respond to sophisticated cyber threats. Combining SIEM with other tools and leveraging automation allows security teams to be more proactive and efficient in their threat hunting efforts. However, it’s crucial to remember that threat hunting is an ongoing process that requires continuous learning, adaptation, and investment in skilled security personnel.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SIEM
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.