Latest Blogs
By AMSAT April 17, 2024
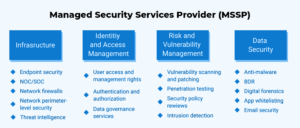
Key points to consider when hiring a Managed Security Services Provider (MSSP)
A managed security service provider (MSSP) offers significant advantages for many businesses. In fact, hiring one can mean you no longer have to worry about risks that an organization is ill-equipped to handle for various reasons, including a shortage of resources or expertise. Seeking a professional provider enables employees to focus on their own key tasks, without taking on the additional responsibility of ensuring security. The following blog post serves as a comprehensive guide to help you identify the key attributes of a top-notch MSSP.
Reputation
Your company’s reputation is pivotal to your business’s success; therefore, it should not be underestimated. It is imperative to ensure that the team entrusted with safeguarding your assets is proficient in their duties and capable of delivering exceptional results.
Asking important questions will help: determine how long a possible provider has been active in the industry and look at feedback they’ve received from other customers. A provider’s status will give you a good idea of their capabilities, and by doing a little bit of research, you can ensure that they’ll be able to deal with your security challenges.
A sound understanding of your business
A good provider should always have a sound understanding of your business and the rules and regulations that must be followed within it. It is important for them to take these guidelines seriously and ensure that key data is secured, allowing your business to continue to protect its customers. Make sure that any potential provider is committed to complying with your business’s specific requirements.
Service level
It’s important to find a provider that offers high quality service. While this may sound too good to be true, MSSPs differ in the service level they provide, and not all will fit your company’s needs. Some providers offer a full incident response system, while others focus exclusively on supervising for intrusions. Some will have knowledge in specific fields of security, which may or may not be valuable to you, depending on what you’re looking for.
Customer support
Customer support is the key element of a quality managed security services provider. In addition to the much-needed support, the level of help provided should also be of the highest quality. After all, you want a provider to explain several procedures and respond to a number of questions. If you’re not getting adequate support from an MSSP, it’s better to look for other alternatives.
Security measures
A competent security provider will always be watchful about new threats, keeping their defense methods up-to-date as security threats change and new technologies evolve. It’s essential that you seek out a quality security provider who is always ahead of the curve, positively impacting your business.
Conclusion
Staying protected is key to the survival of any business, so ensure to conduct thorough research when hiring a new MSSP. No one can take the security of their company for granted; consequently, relying on mediocre MSSPs to save a few hundred bucks will do more harm than good, ultimately contributing to their business’s decline.
TAGS
- Managed Security Services
- Cyber Security Updates
- Cyber Security Providers
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.
Latest Blogs

By AMSAT Mar 16, 2024
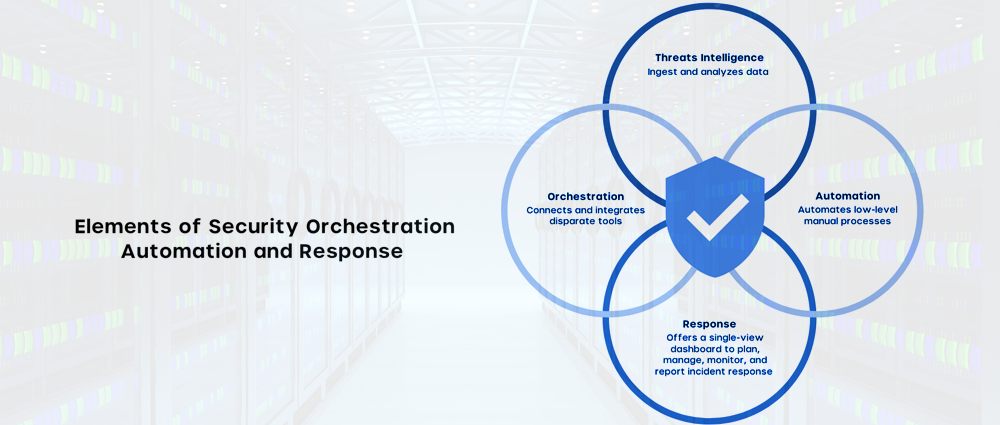
Integrate SOAR with SIEM for Automated Threat Response
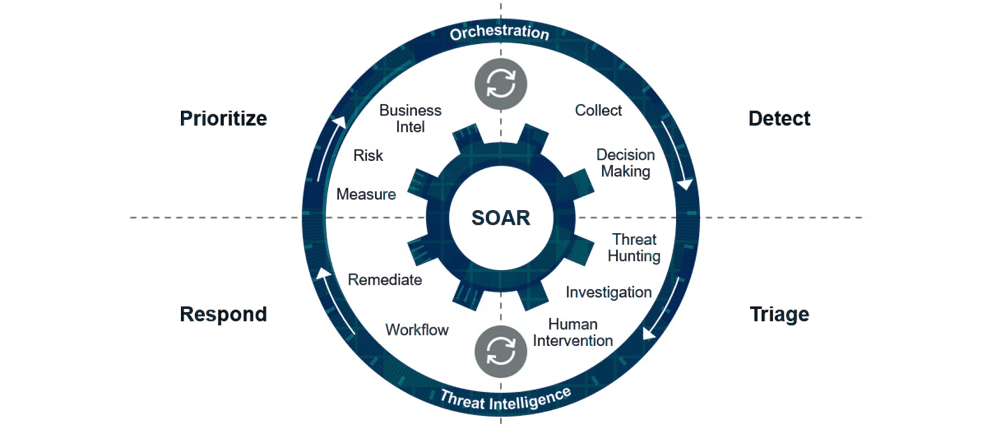
In today’s fast-evolving threat landscape, security teams are constantly bombarded with a volley of alerts. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems are built to sift through these alerts and detect potential security incidents. But there’s a catch: It’s even challenging for SIEM to keep up with the rising volume and complexity of threats. So, how to solve this conundrum? The answer lies in implementing Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR), which offers a powerful solution for automated threat response.
What is SOAR in Cybersecurity?
Short for Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response, SOAR is a platform that integrates various security tools and automates repetitive tasks within an incident response workflow.
Here’s a breakdown of its functionalities:
- Security Orchestration: SOAR streamlines workflows by coordinating actions across different security tools, eliminating the need for manual switching between tools and saving analysts valuable time.
- Automation: SOAR automates repetitive tasks such as data enrichment, investigation steps, and containment procedures, allowing analysts to focus on complex investigations and decision-making.
- Response: SOAR facilitates a faster and more consistent response to security incidents. By automating initial steps and providing analysts with relevant context, SOAR empowers teams to respond swiftly and effectively.
Benefits of SIEM with SOAR Integration
Integrating SIEM and SOAR ensures a powerful combination that massively improves your security posture. Here’s how:
- Faster Threat Detection and Response: SIEM excels at collecting and analyzing security data to detect potential threats. When integrated with SOAR, these alerts trigger automated workflows, accelerating investigation and containment. This translates to a reduced Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) for security incidents.
- Reduced Analyst Workload: SOAR can automate manual tasks, such as data gathering and preliminary investigation steps, freeing up experts’ time to focus on higher-level analysis, threat hunting, and incident resolution.
- Improved Incident Response Consistency: SOAR automates predefined workflows for different incident types, ensuring a steady and repeatable response approach. This minimizes human error and ensures all incidents are addressed effectively.
- Enhanced Security Visibility: SIEM and SOAR work together to provide a comprehensive view of your security environment. By correlating data from various sources, the integrated system offers a deeper understanding of threats and potential attack vectors.
- Streamlined Security Operations: Integrating SIEM and SOAR leads to a more streamlined security operation. Automated workflows and centralized management of alerts improve overall efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Integrate SIEM with SOAR Platforms
The specific steps for integrating SIEM and SOAR will vary depending on the chosen platforms. However, here’s a general framework to follow:
Planning and Analysis:
- Define your goals for integration. What specific security challenges are you trying to address?
- Analyze your existing security infrastructure: SIEM capabilities, SOAR features, and other security tools you use.
- Identify data flows and communication protocols between SIEM and SOAR.
Implementation:
- Configure SIEM to collect and analyze relevant security data. Establish log sources, correlation rules, and alerts for potential incidents.
- Configure SOAR workflows for incident response, automation, and integration with other security tools.
- Establish secure communication channels between SIEM and SOAR to ensure seamless data exchange.
Testing and Validation:
- Thorough testing of the integration is crucial. Simulate various security scenarios and validate automated workflows.
- Ensure proper logging and auditing mechanisms are in place to monitor the integrated system’s performance.
Best Practices for SIEM with SOAR Integration
- Start with Clear Goals: Establish specific objectives for the integration to guide configuration and measure success.
- Standardize Data Format: Ensure consistent data format across SIEM and SOAR for seamless data exchange and accurate analysis.
- Prioritize High-Value Alerts: Configure SIEM to prioritize alerts that require SOAR automation to minimize unnecessary workflows.
- Maintain User Roles and Permissions: Define clear roles and permission access within SIEM and SOAR for optimal security and control.
- Invest in Training: Train security analysts on using the integrated platform effectively.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Continuously monitor the performance of the integrated system and make adjustments as needed based on new threats and security requirements.
Conclusion
Integration of SIEM and SOAR can help organizations achieve a major leap forward in their security posture. Faster threat detection, automated response workflows, and improved analyst efficiency all contribute to a more secure and resilient IT environment. Nevertheless, proper planning, implementation, and best practices are key to unlocking the full potential of this powerful combination.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SIEM
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.
Latest Blogs

By AMSAT Mar 12, 2024
Advanced Threat Hunting Strategies using SIEM Analytics
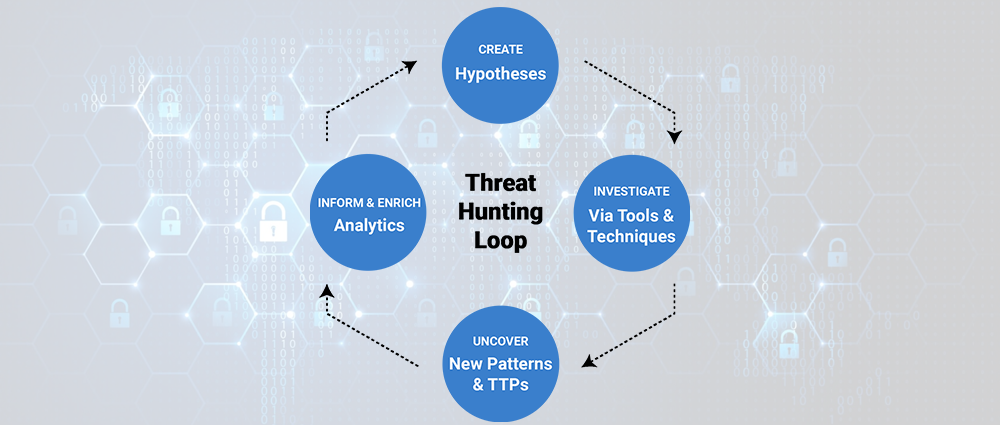
In today’s dynamic cyber threat landscape, traditional security solutions often fall short in detecting sophisticated attacks. Cybercriminals constantly adapt their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to bypass signature-based defenses. This is where cyber threat hunting comes in.
Threat hunting is a proactive approach to exposing hidden threats within an organization’s network. It involves using a combination of human expertise and security tools to actively search for malicious activity. SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) plays a crucial role in threat hunting SIEM by centralizing and analyzing security data from various sources, providing valuable insights for threat hunters.
Why use SIEM for Threat Hunting?
SIEMs offer several advantages for threat hunting:
- Centralized Data Collection: SIEMs aggregate logs and events from diverse security tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and endpoints, providing a single pane of glass for data analysis. This eliminates the need for manual data collection from disparate sources, saving time and effort.
- Data Normalization: SIEMs normalize log data into a consistent format, allowing threat hunters to easily analyze and compare data from various sources even if they have different formats and structures.

- Advanced Analytics: SIEMs offer advanced analytics capabilities, including filtering, correlation, and aggregation, allowing threat hunters to identify anomalies and patterns that might indicate malicious activity.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: SIEMs can integrate with threat intelligence feeds, which provide information on known indicators of compromise (IoCs) and attacker TTPs. This helps threat hunters focus their efforts on high-risk activities and potential threats.
Advanced Threat Hunting Strategies with SIEM Analytics
Here are some advanced threat hunting strategies that leverage SIEM analytics:
- Hypothesis-Driven Hunting: This involves formulating specific hypotheses about potential threats based on industry trends, intelligence reports, or internal risk assessments. Threat hunters then use SIEM queries and analytics to search for evidence supporting or refuting their hypotheses. For example, a hypothesis might be: “Employees in the finance department are at a higher risk of spear phishing attacks.” The threat hunter can then use SIEM queries to analyze email logs and identify suspicious activity related to the finance department.
- Behavioral Analysis: SIEMs can be used to analyze user behavior patterns and identify deviations from the norm. Unusual activity like excessive login attempts, unauthorized access to sensitive data, or lateral movement within the network might indicate a potential compromise.
- Hunting for Unknown Threats: SIEMs can be utilized to identify unknown threats that haven’t been detected by traditional security solutions. This involves analyzing log data for anomalies such as:
- Unusual file transfers
- Unauthorized access attempts
- Unexpected network traffic patterns
- High-risk system activities
- Using the MITRE ATT&CK Framework: This framework categorizes attacker TTPs into various tactics and techniques. By leveraging SIEM analytics and searching for specific elements of the ATT&CK framework within log data, threat hunters can identify potential attack stages and investigate further.
Combining SIEM with Other Threat Hunting Tools
While SIEM is a powerful tool for threat hunting, it’s important to remember that it’s not a standalone solution. Threat hunters often utilize additional tools in conjunction with SIEM to gain a more comprehensive view of the security landscape. Some of these tools include:
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Provides real-time visibility and control over endpoints within the network.
- Network Traffic Analysis (NTA): Analyzes network traffic to identify malicious activities like malware communication and suspicious data exfiltration.
- User Entity and Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Analyzes user and entity behavior to identify potential insider threats or compromised accounts.
Automating Threat Hunting with SIEM
While there’s no substitute for human expertise in threat hunting, automated threat hunting can be a valuable tool to streamline the process and reduce the burden on security analysts. SIEMs can be configured to generate alerts based on pre-defined rules and indicators. These alerts can then be reviewed and investigated by analysts, allowing them to focus on high-priority incidents.

Conclusion
By adopting cutting-edge threat hunting strategies using SIEM analytics, organizations can significantly improve their ability to detect and respond to sophisticated cyber threats. Combining SIEM with other tools and leveraging automation allows security teams to be more proactive and efficient in their threat hunting efforts. However, it’s crucial to remember that threat hunting is an ongoing process that requires continuous learning, adaptation, and investment in skilled security personnel.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SIEM
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.
Latest Blogs

By AMSAT Mar 05, 2024
Centralize Logs with SIEM for Compliance and Threat Detection
In today’s complex IT landscape, security professionals face a constant struggle: maintaining compliance and detecting threats amidst a sea of disparate data. This data, often in the form of logs, originates from various sources like servers, firewalls, applications, and user activity. Without proper organization and analysis, these logs quickly become an overwhelming burden, hindering both compliance efforts and threat detection capabilities.
This is where Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) emerges as a game-changer. By centralizing logs with SIEM, organizations can transform scattered data into actionable insights, paving the way for efficient compliance and robust threat detection.
SIEM Log Management
SIEM log management goes beyond mere log collection. It offers a comprehensive suite of functionalities, including:
Centralized Log Collection: SIEM acts as a central hub, ingesting logs from diverse sources across the IT infrastructure. This eliminates the need to manage individual log files on each device, streamlining data access and analysis.
Normalization and Parsing: SIEM normalizes the format of collected logs, regardless of their origin. This facilitates easier searching, correlation, and analysis across diverse data sets.
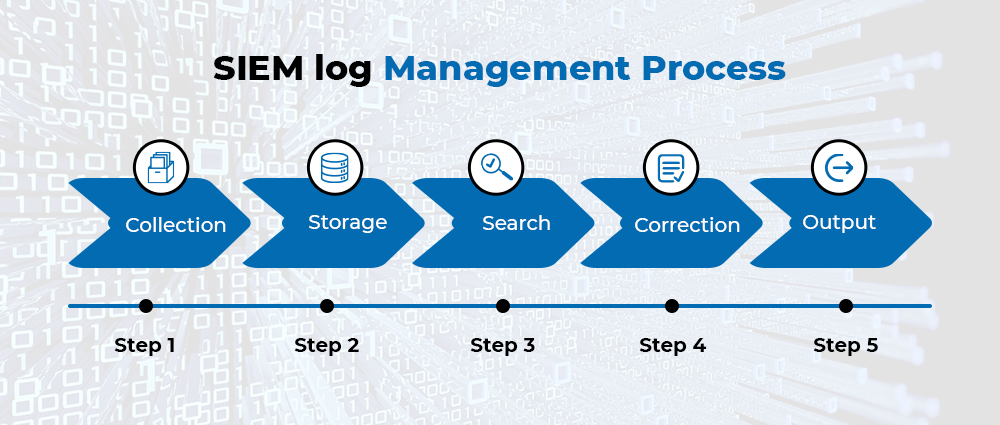
Log Analysis and Correlation: SIEM goes beyond simple storage. It employs advanced algorithms to analyze and correlate log events across different sources. This enables the identification of patterns and anomalies that might indicate potential security incidents.
Threat Detection and Alerts: Leveraging threat intelligence feeds and correlation rules, SIEM can detect suspicious activities and trigger real-time alerts, allowing security teams to swiftly respond to potential threats.
Compliance Reporting: SIEM simplifies compliance by providing consolidated reports on security events and user activity, demonstrating adherence to regulatory requirements.
SIEM and Log Management
While compliance is a crucial aspect, SIEM offers far more significant benefits:
Improved Threat Visibility: By centralizing and analyzing logs, SIEM provides a holistic view of security events across the entire IT environment. This enables security teams to identify and respond to threats more effectively, minimizing potential damage.
Faster Incident Response: SIEM automates alert generation and prioritization based on pre-defined rules, allowing security teams to focus on real threats and expedite incident response times.
Enhanced Security Posture: By providing comprehensive insights into security events, SIEM empowers organizations to identify vulnerabilities and implement proactive security measures to strengthen their overall security posture.

SIEM Log Analysis
SIEM log analysis plays a critical role in extracting valuable insights from collected data. Through various methods such as:
Real-time analysis: Monitoring logs in real-time allows for immediate detection and response to ongoing threats.
Historical analysis: Analyzing historical logs helps identify trends, patterns, and potential security gaps that might not be evident in real-time analysis.
Forensic analysis: In case of a security incident, historical log data can be used for forensic investigation to understand the root cause and identify the attacker’s actions.

By combining these analysis techniques, SIEM empowers security teams to gain a deeper understanding of their security landscape, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and prioritize their efforts effectively.
Conclusion
Centralizing logs with SIEM is an investment that yields significant ROI for organizations striving for both robust compliance and proactive threat detection. By streamlining log management, facilitating comprehensive analysis, and providing actionable insights, SIEM empowers organizations to navigate the ever-evolving security landscape with confidence.
It’s worth noting that effective SIEM log management requires careful planning, implementation, and ongoing maintenance. However, the benefits reaped in terms of improved security posture, faster incident response, and efficient compliance management make SIEM an indispensable tool for any organization looking to secure its IT infrastructure in today’s digital age.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SIEM
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.
Latest Blogs
By AMSAT Feb 29, 2024
5 Key SIEM Architecture Design Best Practices for Optimization and Scalability
In today’s precarious and unpredictable security world, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions have become a crucial line of defense for organizations of all sizes. By centralizing log data from various security tools and systems, SIEMs provide valuable insights into possible security threats and incidents. However, for a SIEM to be truly effective, it needs an optimized and scalable architecture that can deal with the high volume, velocity, and variety of security data.
This blog will explore five key SIEM architecture design best practices that can greatly improve the performance, efficiency, and scalability of your SIEM implementation.
Define Clear Data Collection and Retention Policies:
The foundation of any robust SIEM architecture lies in a well-defined data collection and retention strategy. This strategy outlines the types of data to be collected from various sources, the format and structure of the data, and the duration for which it needs to be retained.
- Prioritize Data Collection: Not all data is created equal. Start by identifying the most critical security information from your diverse security tools, firewalls, operating systems, and applications. Focus on collecting logs related to user activity, system events, network traffic, and access control changes.
- Standardize Log Formats: Ensure consistency in the format and structure of collected logs. This simplifies data parsing and analysis within the SIEM and facilitates efficient storage and retrieval. Common log formats like CEF (Common Event Format) and syslog can be adopted for consistent data ingestion.
- Implement Retention Policies: Define clear retention policies for different types of log data based on legal and compliance requirements, as well as the potential value of the data for future investigations. This helps manage storage space and optimizes SIEM performance by preventing it from being overwhelmed by irrelevant or outdated data.

Leverage Log Parsing and Enrichment:
Raw log data often lacks context and requires additional processing to extract valuable security insights. This is where log parsing and enrichment come into play.
- Log Parsing: SIEMs typically employ parsing rules to extract relevant information from log data, such as timestamps, usernames, IP addresses, event types, and specific details related to the event. Standardized log formats can simplify parsing, while custom parsing rules may be necessary for unique log sources.
- Log Enrichment: Enrich your logs by correlating them with external data sources, such as threat intelligence feeds, vulnerability databases, and user directories. This enriches context and helps the SIEM identify potential threats and prioritize security incidents effectively.
Implement Data Normalization and Aggregation:
Normalizing and aggregating data helps optimize storage and enhance query performance within your SIEM.
- Data Normalization: Normalize log data by converting it into a consistent format. This eliminates inconsistencies and redundancies, allowing for efficient storage and analysis.
- Data Aggregation: Aggregate similar events or logs based on specific criteria, such as timestamps, severity levels, or source systems. This helps reduce data volume and simplifies query execution, improving overall SIEM performance.
Design a Scalable Architecture:
As your organization grows, the volume and variety of security data collected by your SIEM will inevitably increase. To ensure continued performance and maintainability, your SIEM architecture needs to be scalable.
- Consider a Distributed Architecture: A distributed architecture distributes data processing and storage across multiple nodes, allowing for horizontal scaling. This enables the SIEM to handle increasing data volumes without compromising performance.
- Utilize Cloud-Based SIEM Solutions: Cloud-based SIEM solutions offer inherent scalability and flexibility. They leverage the cloud provider’s infrastructure, automatically scaling resources up or down to meet your evolving needs.
Integrate SIEM with Security Tools and Workflows:
SIEMs operate most effectively when integrated with other security tools and workflows. This enables a holistic view of the security landscape and streamlines incident response processes.
- SIEM Integration: Integrate your SIEM with security tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and vulnerability scanners. This allows for centralized monitoring and correlation of security events across your entire security stack.
- Automate Workflows: Automate routine tasks within your SIEM, such as log collection, parsing, and alert generation. This frees up security personnel to focus on more complex investigations and incident response activities.
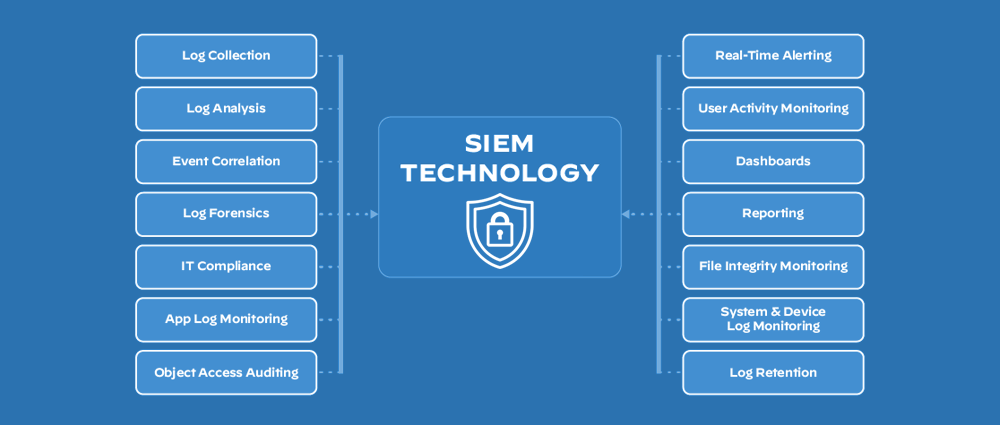
SIEM Logging Best Practices
In addition to the architectural considerations, adhering to best practices for SIEM logging can further improve the effectiveness and efficiency of your SIEM solution.
- Collect all relevant security logs: Ensure comprehensive log collection to provide a complete picture of security-related activity across your environment.
- Maintain data integrity: Implement measures to ensure the accuracy and completeness of collected logs to avoid misleading information or gaps in security visibility.
- Regularly review and update log sources: As your security landscape evolves, so too should your log collection strategy. Regularly review and update log sources to ensure continued relevance and capture new security events.
Conclusion
In today’s volatile threat scene, nothing is more important than optimizing and scaling your SIEM architecture. By following the key best practices mentioned in this blog, you can ensure your SIEM efficiently collects, processes, and analyzes security data, providing valuable insights to fortify your organization’s overall cybersecurity posture.
A well-designed and optimized SIEM is not just a tool, but a strategic investment that empowers your security team to stay ahead of evolving threats and keep your organization safe.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SIEM
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.
Latest Blogs

By AMSAT Feb 20, 2024
Top 5 SIEM Use Cases Decoded: Security Monitoring, Threat Detection, Compliance Reporting and More
In today’s dynamic and precarious digital landscape, nothing can be more important than securing your organization’s critical data and infrastructure. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions have emerged as a pivotal tool in this battle, offering centralized log collection, analysis, and threat detection capabilities. But how exactly do you maximize the value of your SIEM investment? Understanding the key SIEM use cases is key.
What is a SIEM Use Case?
A SIEM use case defines a specific security challenge or objective that the SIEM can address. By tailoring your SIEM configuration and analysis to these use cases, you can optimize its effectiveness in protecting your organization.

Top 5 SIEM Use Cases
Continuous Security Monitoring:
- Real-time visibility: SIEMs ingest logs from diverse sources, providing a consolidated view of activity across your IT environment. This real-time visibility enables you to detect suspicious events as they occur, preventing potential breaches from escalating.
- Log correlation and analysis: Powerful correlation engines within SIEMs analyze log data for anomalous patterns or deviations from established baselines. This helps identify potential threats hidden within seemingly normal activity.
- Security dashboards and alerts: Customizable dashboards offer a real-time overview of security posture, while automated alerts notify you of suspicious events requiring immediate attention. This allows your security team to prioritize and respond to threats quickly.
Advanced Threat Detection:
- Threat intelligence integration: SIEMs can integrate with threat intelligence feeds, enriching log data with known indicators of compromise (IOCs) and attack patterns. This helps detect sophisticated threats that might otherwise evade traditional signature-based defenses.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): UEBA leverages machine learning to analyze user and entity behavior patterns within your network. This helps identify anomalies indicative of compromised accounts or insider threats.
- Advanced hunting capabilities: SIEMs offer powerful search and investigation tools, allowing security analysts to hunt for specific threats based on historical data or emerging intelligence. This proactive approach empowers rapid threat neutralization.
Streamlined Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM):
- Incident response workflow: SIEMs can automate incident response workflows, streamlining tasks like evidence collection, containment, and eradication. This reduces response time and minimizes damage from security incidents.
- Forensic analysis: Log data stored within the SIEM serves as a valuable resource for forensic investigations, helping determine the root cause of incidents and identify attackers.
- Reporting and compliance: SIEMs generate detailed reports on security incidents, providing valuable insights for security teams and auditors. This simplifies compliance audits and demonstrates adherence to regulatory requirements.

Enhanced Security Operations Center (SOC) Efficiency:
- Centralized log management: SIEMs eliminate the need to manage logs from individual systems, simplifying log collection and analysis for SOC teams. This improves team efficiency and reduces administrative overhead.
- Collaboration and communication: SIEMs provide a central platform for SOC teams to share information and collaborate on investigations. This enhances team communication and streamlines incident response.
- Improved situational awareness: Real-time dashboards and alerts keep SOC teams informed of potential threats, allowing them to prioritize their efforts effectively.
Regulatory Compliance and Reporting:
- Compliance mandates: Many data privacy regulations, like GDPR and HIPAA, require organizations to log and audit user activity. SIEMs facilitate compliance by collecting and storing relevant logs.
- Pre-built compliance reports: SIEMs often come pre-configured with reports aligned with specific compliance requirements, simplifying the reporting process.
- Demonstrating compliance posture: Detailed security reports generated by SIEMs provide evidence of your organization’s adherence to compliance regulations.
Unlocking the Value of SIEM Use Cases
Understanding and implementing relevant SIEM use cases is crucial for maximizing your security posture. By leveraging the capabilities outlined above, you can achieve:
- Enhanced threat detection and prevention: Identify and neutralize threats faster, minimizing their impact.
- Improved security incident response: Streamline incident response processes and reduce the time to resolution.

- Simplified compliance reporting: Demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements with ease.
- Elevated SOC efficiency: Empower your SOC team with the tools and information they need to operate effectively.
Conclusion
SIEM use cases are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Tailor your approach to your specific security needs and resources. By strategically leveraging SIEM capabilities, you can gain deeper situational awareness and insights into your security posture, enabling you to proactively identify and mitigate threats.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SIEM
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.
Latest Blogs
By AMSAT Feb 14, 2024
On-Premise vs Cloud-Based SIEM: Which is Right for You?
In today’s ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, organizations are constantly faced with a considerable challenge: to detect and respond to threats effectively. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions play a pivotal role in achieving this objective by aggregating and examining data from various sources to identify potential security incidents. However, when choosing a SIEM solution, it’s critical to choose between on-premise and cloud-based SIEM solutions, as both of them offer unique advantages and drawbacks.
This blog will explore the key considerations for choosing between these two deployment models, helping you select the solution that best aligns with your organization’s security needs and infrastructure.

On-Premise SIEM
An on-premise SIEM provides complete control over the data and infrastructure. You house the hardware and software on-site, giving you full autonomy over data security, customization, and compliance. This approach is often favored by organizations in highly regulated industries with strict data privacy requirements.
Advantages of On-Premise SIEM
Data Sovereignty: Maintain complete control and visibility over where your data resides and who has access to it.
Customization: Tailor the SIEM to your specific needs and integrate it seamlessly with existing infrastructure.
Compliance: Ensure adherence to specific compliance regulations that may have restrictions on cloud storage.
Disadvantages of On-Premise SIEM
High Cost: Requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT staff for deployment, maintenance, and upgrades.
Scalability: Scaling resources to accommodate growing data volumes or security needs can be challenging and expensive.
Management Burden: Demands dedicated IT expertise for constant maintenance, software updates, and infrastructure management.
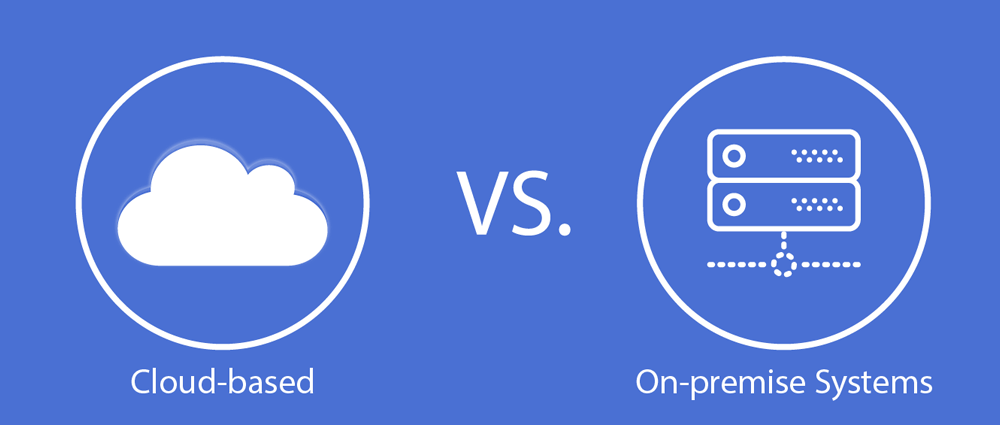
Cloud-Based SIEM
Cloud-based SIEM, also known as cloud SIEM or cloud-native SIEM, leverages the infrastructure and expertise of cloud providers. Your data and SIEM application reside in the cloud, offering scalability, accessibility, and potentially lower operational costs.
Advantages of Cloud-Based SIEM
Lower Cost: Eliminates upfront hardware investment and reduces IT staff requirements for maintenance and upgrades.
Scalability: Easily scale resources to accommodate changing data volumes and security needs with a pay-as-you-go model.
Faster Deployment: Get up and running quickly with minimal IT involvement, often through subscription-based services.
Automatic Updates: Benefit from regular software updates and threat intelligence automatically deployed by the provider.
Accessibility: Access the SIEM and security data from anywhere with an internet connection.
Disadvantages of Cloud-Based SIEM
Data Security Concerns: Some organizations may be apprehensive about entrusting sensitive data to a third-party cloud provider.
Limited Customization: The level of customization might be restricted compared to on-premise solutions.
Vendor Lock-in: Switching providers can be complex due to data migration challenges and potential API incompatibilities.
Making the Right Choice
Ultimately, the decision between on-premise and cloud-based SIEM depends on your organization’s specific needs and priorities. Here are some key factors to consider:

Data Sensitivity: For highly sensitive data, on-premise might offer greater control and peace of mind.
IT Expertise: If you have limited IT resources, a cloud-based solution’s ease of deployment and management might be more attractive.
Scalability Needs: If your data volume or security demands fluctuate frequently, cloud-based scalability can be advantageous.
Budget Constraints: Consider the overall cost, including upfront investments, ongoing maintenance, and IT staff requirements.
Compliance Regulations: Ensure your chosen solution aligns with any relevant data privacy and security regulations.
Some organizations opt for a hybrid approach, combining both on-premise and cloud-based SIEM deployments. This strategy can offer a balance between data control and scalability, but it requires careful planning and integration to ensure seamless security monitoring.
Summary
Both on-premise and cloud-based SIEM solutions offer unique advantages and cater to different organizational needs. By carefully evaluating your priorities, resources, and security requirements, you can make an informed decision that empowers your organization to effectively detect and respond to security threats in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SIEM
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.
Latest Blogs

By AMSAT Feb 07, 2024
Choosing the Best SIEM Solution: A Comprehensive Review
In today’s ever-escalating threat landscape, organizations constantly generate a torrent of security data – logs, events, incidents – from various sources. Managing and analyzing this data effectively is key to detecting and responding to security threats swiftly. That’s where Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions come into play.
What is SIEM?
SIEM software centralizes security data from diverse sources, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), endpoint security tools, applications, and network devices. It aggregates, analyzes, and correlates this data in real-time, providing insights into potential security incidents. SIEM offers features like:
Log collection and aggregation: Gathers security data from disparate sources into a single repository for centralized analysis.
Real-time and historical analysis: Continuously monitors incoming data for suspicious activity and provides historical insights for threat hunting and forensic investigations.
Alerts and notifications: Generates timely alerts based on predefined rules and threat intelligence, enabling rapid response to potential incidents.
Incident investigation and management: Automates incident triage and investigation workflows, saving time and resources.
Security reporting and compliance: Provides comprehensive reports on security posture and helps organizations meet compliance requirements.

Understanding Your Needs
Choosing the right SIEM solution isn’t a one-size-fits-all scheme. Your organization’s specific needs and requirements play a crucial role. Consider factors like:
Security environment: Assess your IT infrastructure complexity, data volume, and specific security challenges.
Budget: SIEM solutions can range from open-source options to premium enterprise tools. Set a realistic budget that aligns with your needs.
Expertise: Evaluate your internal technical resources and expertise to maintain and operate the SIEM solution.
Integrations: Ensure the SIEM integrates seamlessly with your existing security tools and infrastructure.
Scalability: Choose a solution that can scale with your organization’s growth and evolving security needs.
SIEM Software: Open Source vs. Commercial
Both open-source and commercial SIEM solutions have their advantages and disadvantages:
Open Source SIEM:
Cost-effective: Free to use, reducing licensing costs significantly.
Customization: Provides flexibility to customize and modify the solution to meet specific needs.
Community support: Benefits from a vibrant community of developers and users for troubleshooting and updates.
Technical expertise required: Installation, configuration, and maintenance require in-house technical expertise.
Limited features: May lack advanced features and functionalities compared to commercial solutions.
Security updates: Relying on community volunteers for security updates might raise concerns for some organizations.

Popular Open Source SIEM Tools
Elastic Stack: Highly scalable and customizable, but requires significant technical expertise.
OSSEC: Free and open-source HIDS/HONEYC system with basic SIEM capabilities.
Security Onion: Debian-based distribution combining several open-source security tools with SIEM functionality.
Commercial SIEM:
Comprehensive features: Offer a wider range of features and functionalities like advanced threat intelligence, machine learning, and automation.
Vendor support: Provides dedicated support from the vendor for installation, configuration, and maintenance.
User-friendly: Often come with user-friendly interfaces and pre-configured rules, reducing the need for extensive technical expertise.
Scalability: Designed to scale with your organization’s growing security needs.
Cost: Licensing fees can be significant, depending on the chosen solution and its features.
Popular Commercial SIEM Tools:
McAfee SIEM: Offers threat intelligence, user behavior analytics, and advanced reporting capabilities.
Splunk Enterprise: Highly scalable and customizable platform with a wide range of integrations.
ArcSight SIEM: Integrates well with other ArcSight security products and offers machine learning-powered threat detection.
LogRhythm SIEM: User-friendly interface with automation capabilities and pre-built content for various use cases.
Managed SIEM Providers
For organizations lacking internal expertise or resources, managed SIEM services can be a valuable option. These providers offer:
SIEM solution deployment and management: Take care of installation, configuration, and ongoing maintenance of the SIEM solution.
Security expertise: Provide dedicated security analysts to monitor and analyze security events, detect threats, and respond to incidents.
Cost-effectiveness: Can be more cost-effective than building and maintaining an internal SIEM team.

Key Statistics
According to Gartner, the global SIEM market is expected to reach $9.44 billion by 2025, highlighting the growing demand for these solutions. A study by IBM revealed that 95% of security professionals believe SIEM is crucial for incident detection and response. However, another study by SANS Institute found that 53% of organizations struggle to effectively utilize their SIEM solutions, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right SIEM solution and implementing it effectively.
Summary
Choosing the best SIEM solution requires careful deliberation of your organization’s unique needs, budget, and technical expertise. By weighing the advantages and disadvantages of open-source vs. commercial options, evaluating managed SIEM services, and understanding the critical factors involved, you can make an informed decision that strengthens your security posture and safeguards your valuable data. SIEM is an investment, and its effectiveness hinges on your commitment to implementation, best practices, and continuous improvement.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SIEM
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.
Latest Blogs

By AMSAT Feb 02, 2024
Ultimate Guide to Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
In today’s ever-escalating cyber landscape, businesses encounter a fusillade of threats, from devastating malware attacks to data breaches and social engineering. But navigating this complex environment is not a walk in the park—it requires watchful monitoring and effective security solutions. That’s where Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) comes into play.
What is SIEM?
SIEM is a powerful tool that collects, aggregates, and analyzes data from various security sources across your IT infrastructure. This includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), endpoints, applications, and cloud environments. By centralizing and correlating this data, SIEM paints a comprehensive picture of your security posture, enabling you to detect and respond to threats swifter and more effectively.
Key Features of SIEM:
- Log Management: Consolidate logs from various sources for centralized analysis.
- Security Event Monitoring: Detect suspicious activity in real-time through continuous log monitoring.
- Incident Response: Facilitate quick response to security incidents through alerts and investigation tools.
- Threat Intelligence: Leverage threat intelligence feeds to gain insights into emerging threats.
- Compliance Reporting: Generate reports to meet compliance requirements (e.g., PCI DSS, HIPAA).
Benefits of Implementing SIEM:
- Improved Threat Detection: Identify and respond to security incidents faster.
- Enhanced Security Visibility: Gain a centralized view of your security posture.
- Reduced Investigation Time: Streamline investigations and shorten security breach response times.
- Better Compliance Management: Simplify compliance reporting with centralized log management.
- Simplified Security Operations: Streamline workflows and improve operational efficiency.
Advanced Event System
Modern SIEM solutions go beyond basic log management, incorporating advanced event correlation techniques. This allows them to identify relationships between seemingly unrelated events, providing deeper context and helping you distinguish genuine threats from noise.
SIEM as a Service (SIEMaaS):
Traditional SIEM deployments require significant infrastructure and expertise. However, SIEM as a Service (SIEMaaS) offers a cloud-based alternative, eliminating the need for on-premise hardware and management. This model benefits organizations of all sizes, especially those with limited IT resources, by:
- Reducing upfront costs: Pay-as-you-go model eliminates the need for substantial upfront investments.
- Faster deployment: Get started quickly with minimal configuration and maintenance.
- Scalability: Easily scale your SIEM solution to meet evolving security needs.
- Expertise access: Leverage the vendor’s expertise in managing and maintaining the SIEM environment.
Managed SIEM Services:
For organizations seeking further support, Managed SIEM services provide comprehensive solutions. These services involve a team of security experts who:
- Monitor and manage your SIEM environment 24/7.
- Analyze logs and identify potential threats.
- Investigate and respond to security incidents.
- Provide ongoing guidance and support.
Choosing the Right SIEM Solution:
Selecting the right SIEM solution depends on your specific needs and resources. Consider factors like:
- Organization size and security complexity.
- Budget and deployment options (on-premise, cloud, hybrid).
- Features and functionalities required.
- Ease of use and integration with existing security infrastructure.
Statistics Highlighting the Importance of SIEM:
- According to IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2023, 68% of organizations experienced a security incident in the past year.
- According to the 2023 cost of a data breach report by IBM and the Ponemon institute, the global average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million, a 15% increase over 3 years.
- As per research by Forrester, organizations using SIEM can reduce security incident response time by up to 50%.
Implementing SIEM: Essential Steps
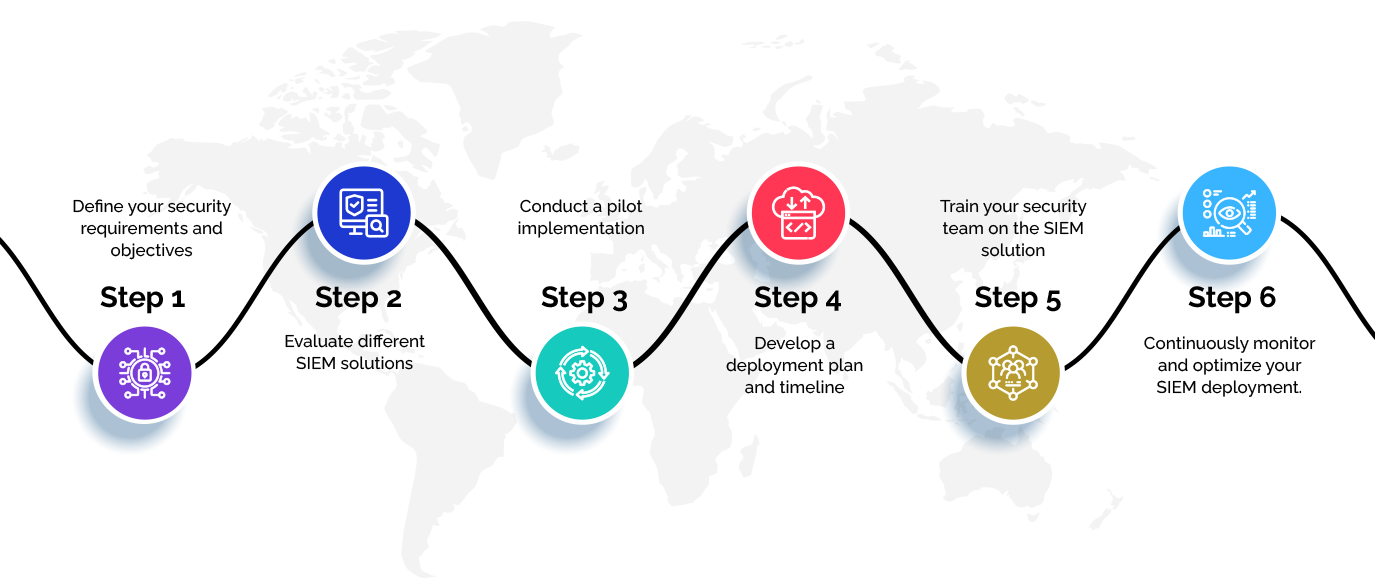
- Define your security requirements and objectives.
- Evaluate different SIEM solutions.
- Conduct a pilot implementation.
- Develop a deployment plan and timeline.
- Train your security team on the SIEM solution.
- Continuously monitor and optimize your SIEM deployment.
Summary
In today’s digital age, SIEM is no longer a luxury but a necessity for any organization serious about securing its data and assets from falling into the hands of malicious actors. Implementation of SIEM solutions tailored to your needs can help you gain valuable insights into your security posture, allowing you to proactively identify and respond to threats, ultimately reducing risk and protecting your business. Organizations can only ignore SIEM at their own peril.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- SIEM
- Cyber Security
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.
Latest Blogs

By AMSAT Jan 26, 2024
Analyzing the Top 3 Emerging Cyber Threats and How to Prepare for the Future
Cyber threat management is a challenge that businesses worldwide are grappling with, especially in the face of the exponential rise in cyber threats. 2023 was a year of continued evolution in the cybersecurity landscape.
According to a survey by The State of Supply Chain Defense Annual Global Insights Reports 2023, the mean number of supply chain breaches experienced 4.16 incidents in 2023, up from 0.89 in 2022. While familiar threats like ransomware persisted, ingenious attackers developed new tactics and exploited emerging technologies, giving security professionals sleepless nights.

According to a report published by the Homeland Security Department’s Cyber Safety Review Board, it’s high time organizations acted to secure themselves, with the Board underlining tangible ways to do so, supported by the U.S. government and the companies best prepared to provide foolproof solutions to elevate the whole ecosystem. As we ring in 2024, it’s crucial to reflect on the past year’s most concerning trends and prepare for the cyber threats that lie ahead.
Top 3 Emerging Cyber Threats of 2023:
1. Supply Chain Attacks:
Traditional attack methods often target the end user directly. However, 2023 saw a surge in supply chain attacks, where attackers compromise a vendor or supplier to infiltrate their customers’ systems. These attacks leverage the inherent trust businesses place in their partners, making them particularly difficult to detect and prevent.
One notable example is the SolarWinds supply chain attack, which affected thousands of organizations worldwide. Hackers infiltrated the software company’s update servers, injecting malicious code into legitimate software updates. This allowed them to gain access to the systems of SolarWinds’ customers, including government agencies and Fortune 500 companies.

2. Deepfakes and Synthetic Media:
The rise of deepfakes and synthetic media presents a major challenge for cybersecurity. These technologies allow threat actors to create highly realistic audio and video fakes, making it increasingly difficult to separate truth from fiction.
Deepfakes can be used for various malicious purposes, such as:
- Social engineering: Attackers can impersonate executives or employees to gain access to sensitive information or trick victims into transferring money.
- Disinformation campaigns: Spreading fake news and propaganda can sow discord and manipulate public opinion.
- Financial fraud: Deepfakes can be used to create fake identities or impersonate victims to commit fraud.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities:
The growing number of IoT devices connected to the internet presents a vast attack surface for cybercriminals. These devices often have weak security measures and are poorly patched, making them easy targets for exploitation. There are over 12 billion connected IoT devices worldwide, and 70% of them have at least one critical vulnerability, according to a study by MDPI.
Once compromised, IoT devices can be used to launch several attacks, including:
- DDoS attacks: Botnets of compromised devices can be used to overwhelm websites and online services with traffic, making them unavailable to legitimate users.
- Data breaches: Attackers can steal sensitive information stored on IoT devices, such as personal data or home security footage.
- Botnet attacks: Compromised devices can be used to launch attacks against other targets, such as critical infrastructure.
Trends in Cybersecurity:
- Increased Focus on Cyber Threat Intelligence: Organizations are increasingly investing in cyber threat intelligence (CTI) to gain insights into attacker tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). This information helps them proactively identify and mitigate threats before they can cause damage.
- Shift to Zero Trust Security: The traditional perimeter-based security model is no longer sufficient in today’s complex IT environments. Organizations are adopting zero trust security principles, which assume that no user or device should be trusted by default and access should be granted based on the least privilege principle.
- Rise of Security Automation: With the volume and sophistication of cyberattacks increasing, security automation is becoming essential. Automated tools can help detect and respond to threats faster and more effectively.
How to Prepare for Future Cyber Threats:
- Conduct Regular Security Assessments: Regularly assess your organization’s security posture to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Implement a Layered Security Approach: Employ a layered security approach that includes endpoint protection, network security, and data security solutions.
- Train Employees on Cybersecurity Awareness: Train your employees on cybersecurity best practices to identify and avoid phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics.
- Have a Cyber Incident Response Plan: Develop and test a cyber incident response plan to outline how you will respond to a security breach.
- Stay Up-to-Date on the Latest Threats: Keep yourself informed about the latest cyber threats and trends by subscribing to security advisories and attending industry events.
List of Companies Affected by Ransomware in 2023:
- Colonial Pipeline: The largest fuel pipeline operator in the United States was forced to shut down operations after a ransomware attack, leading to widespread fuel shortages and price increases.
- Costa Rica: The Costa Rican government declared a national emergency after a series of coordinated ransomware attacks crippled critical infrastructure.
- CNA Financial Corporation: The eighth-largest insurance company in the United States
Conclusion
In today’s ever-evolving threat landscape, businesses are confronted with a plethora of challenges from threat actors that have simply outwitted them in terms of their approach and modus operandi to carry out sophisticated attacks.
Given the complexity and frequency of cyberattacks that have kept businesses on their toes, it would be prudent for entrepreneurs to beef up cybersecurity measures and collaboration among stakeholders, while ensuring consistent ingenuity to stay ahead of potentially devastating threats.
AMSAT, a well-known cybersecurity company, offers a range of services to safeguard your organization from looming cyber threats that could cause it irreparable damage. So, call now or schedule a free demo to see what wonders the company can do to ensure the security of your organization and your employees.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Digital Threats
- Cyber Security
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.