Latest Blogs
By AMSAT Feb 29, 2024
5 Key SIEM Architecture Design Best Practices for Optimization and Scalability
In today’s precarious and unpredictable security world, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions have become a crucial line of defense for organizations of all sizes. By centralizing log data from various security tools and systems, SIEMs provide valuable insights into possible security threats and incidents. However, for a SIEM to be truly effective, it needs an optimized and scalable architecture that can deal with the high volume, velocity, and variety of security data.
This blog will explore five key SIEM architecture design best practices that can greatly improve the performance, efficiency, and scalability of your SIEM implementation.
Define Clear Data Collection and Retention Policies:
The foundation of any robust SIEM architecture lies in a well-defined data collection and retention strategy. This strategy outlines the types of data to be collected from various sources, the format and structure of the data, and the duration for which it needs to be retained.
- Prioritize Data Collection: Not all data is created equal. Start by identifying the most critical security information from your diverse security tools, firewalls, operating systems, and applications. Focus on collecting logs related to user activity, system events, network traffic, and access control changes.
- Standardize Log Formats: Ensure consistency in the format and structure of collected logs. This simplifies data parsing and analysis within the SIEM and facilitates efficient storage and retrieval. Common log formats like CEF (Common Event Format) and syslog can be adopted for consistent data ingestion.
- Implement Retention Policies: Define clear retention policies for different types of log data based on legal and compliance requirements, as well as the potential value of the data for future investigations. This helps manage storage space and optimizes SIEM performance by preventing it from being overwhelmed by irrelevant or outdated data.

Leverage Log Parsing and Enrichment:
Raw log data often lacks context and requires additional processing to extract valuable security insights. This is where log parsing and enrichment come into play.
- Log Parsing: SIEMs typically employ parsing rules to extract relevant information from log data, such as timestamps, usernames, IP addresses, event types, and specific details related to the event. Standardized log formats can simplify parsing, while custom parsing rules may be necessary for unique log sources.
- Log Enrichment: Enrich your logs by correlating them with external data sources, such as threat intelligence feeds, vulnerability databases, and user directories. This enriches context and helps the SIEM identify potential threats and prioritize security incidents effectively.
Implement Data Normalization and Aggregation:
Normalizing and aggregating data helps optimize storage and enhance query performance within your SIEM.
- Data Normalization: Normalize log data by converting it into a consistent format. This eliminates inconsistencies and redundancies, allowing for efficient storage and analysis.
- Data Aggregation: Aggregate similar events or logs based on specific criteria, such as timestamps, severity levels, or source systems. This helps reduce data volume and simplifies query execution, improving overall SIEM performance.
Design a Scalable Architecture:
As your organization grows, the volume and variety of security data collected by your SIEM will inevitably increase. To ensure continued performance and maintainability, your SIEM architecture needs to be scalable.
- Consider a Distributed Architecture: A distributed architecture distributes data processing and storage across multiple nodes, allowing for horizontal scaling. This enables the SIEM to handle increasing data volumes without compromising performance.
- Utilize Cloud-Based SIEM Solutions: Cloud-based SIEM solutions offer inherent scalability and flexibility. They leverage the cloud provider’s infrastructure, automatically scaling resources up or down to meet your evolving needs.
Integrate SIEM with Security Tools and Workflows:
SIEMs operate most effectively when integrated with other security tools and workflows. This enables a holistic view of the security landscape and streamlines incident response processes.
- SIEM Integration: Integrate your SIEM with security tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and vulnerability scanners. This allows for centralized monitoring and correlation of security events across your entire security stack.
- Automate Workflows: Automate routine tasks within your SIEM, such as log collection, parsing, and alert generation. This frees up security personnel to focus on more complex investigations and incident response activities.
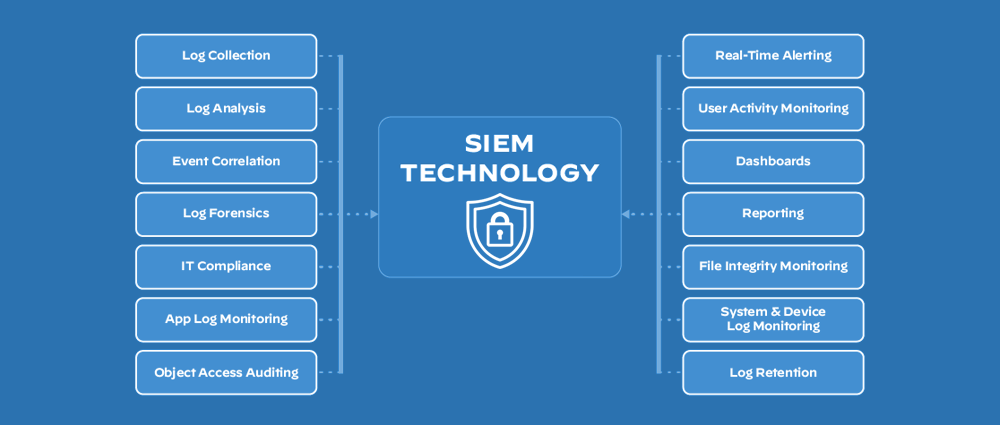
SIEM Logging Best Practices
In addition to the architectural considerations, adhering to best practices for SIEM logging can further improve the effectiveness and efficiency of your SIEM solution.
- Collect all relevant security logs: Ensure comprehensive log collection to provide a complete picture of security-related activity across your environment.
- Maintain data integrity: Implement measures to ensure the accuracy and completeness of collected logs to avoid misleading information or gaps in security visibility.
- Regularly review and update log sources: As your security landscape evolves, so too should your log collection strategy. Regularly review and update log sources to ensure continued relevance and capture new security events.
Conclusion
In today’s volatile threat scene, nothing is more important than optimizing and scaling your SIEM architecture. By following the key best practices mentioned in this blog, you can ensure your SIEM efficiently collects, processes, and analyzes security data, providing valuable insights to fortify your organization’s overall cybersecurity posture.
A well-designed and optimized SIEM is not just a tool, but a strategic investment that empowers your security team to stay ahead of evolving threats and keep your organization safe.
TAGS
- Cyber Threats
- Cyber Security
- SIEM
Recent Blogs
Ready to Get Started?
Our specialists are ready to tailor our security service solutions to fit the needs of your organization.