By AMSAT November 27, 2025
Cloud Security Tips: Best Practices for 2026
Cloud security changes fast. Every year, new tools, new attack methods, and new technologies appear, making it harder for companies to stay secure. And in 2026, things are going to evolve at even more faster rate.
Cybercriminals are taking advantage of AI nowadays, the cloud systems have become very complicated, and the volume of data that is being kept online is tremendously high.
Cloud security is now a must for everyone regardless if you are the one running a small startup or managing a global enterprise. It’s a necessity. This guide presents the most crucial cloud security tips for 2026 in a straightforward and conversational manner, no confusing terms, and no needless intricacy. Just clear and practical advice.
We will assist you in the process of making your cloud environment robust without the fear of getting lost in the smoke.
First, let’s get to the fundamentals.
Comprehending Cloud Security
Cloud security encompasses the technologies, processes, and controls that ensure the safety of your data, workloads, apps, and infrastructure in the cloud. Visualize it as a digital fortress that protects all your data or applications running on cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Cloud security today focuses on:
- Preventing unauthorized access
- Monitoring cloud workloads
- Encrypting sensitive information
- Managing user permissions
- Detecting threats in real time
- Protecting applications from development to deployment
Security is integrated at the cloud level, so modern systems apply cloud-native security. However, it cannot be considered an afterthought. It is necessary because applications are now running in various environments such as containers, Kubernetes, microservices and serverless.
Why Cloud Environments Are Hard to Secure
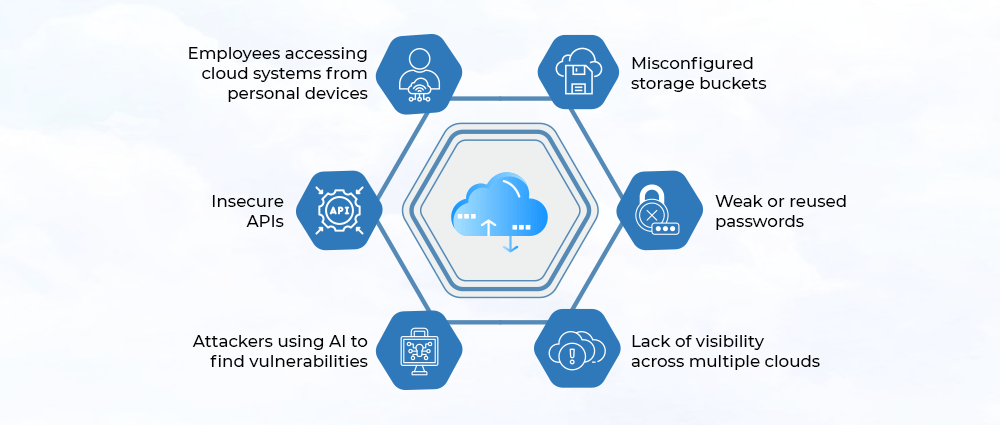
Cloud systems are incredibly flexible. You can scale up, scale down, add services, remove services, everything happens fast. But this speed also creates risks.
In 2026, the biggest cloud security challenges include:
Here you go , I’ve expanded each bullet point with easy, clear, beginner-friendly explanations while keeping the tone conversational.
1. Misconfigured storage buckets
This is one of the most common reasons companies face data leaks. A simple misconfiguration can expose customer information, documents, or internal files without anyone noticing until it’s too late.
Why it happens:
- New team members don’t know the default settings
- Too many people have permission to change settings
- Misconfigurations go unnoticed due to rapid deployments
Hackers constantly scan the internet to find open storage buckets.
2. The use of weak or reused passwords
It is a common practice for employees to use the same password on multiple platforms or to select very weak passwords like 123456, password123, or their name with a number. These passwords are very easy to crack by hackers with the help of automated tools.
Why it happens:
- People want convenience
- Companies don’t enforce strong rules
- No multi-factor authentication (MFA) in place
If an attacker gets just one password, they may gain access to entire cloud accounts, databases, or admin dashboards.
3. Lack of visibility across multiple clouds
Many companies use multiple cloud providers, AWS for apps, Azure for identity, Google Cloud for data analytics. This creates a multi-cloud setup.
The problem?
Each platform has its own dashboard, settings, and logs. You might secure one cloud well but forget something in another, creating blind spots.
Why it happens:
- Teams work separately on different clouds
- No unified monitoring tools
- Too many systems to track manually
If you can’t see everything happening in real time, you cannot stop a breach or detect unusual activity.
4. Attackers using AI
Cybercriminals now use AI tools to automate attacks. These tools can scan cloud systems faster than humans, identify weak settings, and find entry points in seconds.
Examples of how attackers use AI:
- Finding misconfigured servers instantly
- Breaking weak passwords with AI-powered brute force
- Detecting exposed APIs
- Creating more realistic phishing messages
Attackers no longer need to be skilled hackers. AI makes sophisticated attacks accessible to anyone.
5. Insecure APIs
APIs help your apps talk to each other. But if they aren’t protected properly, they can become easy pathways for hackers.
What makes APIs insecure:
- Weak authentication
- Exposed endpoints
- Lack of rate limiting
- Excessive permissions
If someone breaks into one API, they might access entire databases or internal systems connected to it.
6. Unsecured personal devices
With remote and hybrid work, employees access cloud systems using laptops, tablets, and phones. These devices may not be updated or protected.
Risks include:
- Malware on personal devices
- Unsecured Wi-Fi networks (cafés, airports)
- Lost or stolen devices
- Lack of antivirus or firewalls
Even if your cloud is secure, an infected device can give attackers a doorway into your system.
To solve these challenges, companies now rely heavily on Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools that detect misconfigurations and weaknesses early
Why Cloud Security Tips Matter More Than Ever
In today’s world, businesses depend on the cloud for everything, from customer data to mission-critical operations. Weak cloud security doesn’t just lead to minor issues. It can cause:
- Data loss
- Financial penalties
- System downtime
- Customer distrust
- Major compliance violations
Most importantly, cloud threats have become smarter. Hackers don’t just target big enterprises anymore, they go after small and mid-sized companies because they often have weaker defenses.
Whether you’re running a personal project or a multi-billion-dollar company, you need a clear cloud security strategy and a strong cloud security architecture.
Building a Reliable Cloud Security Architecture
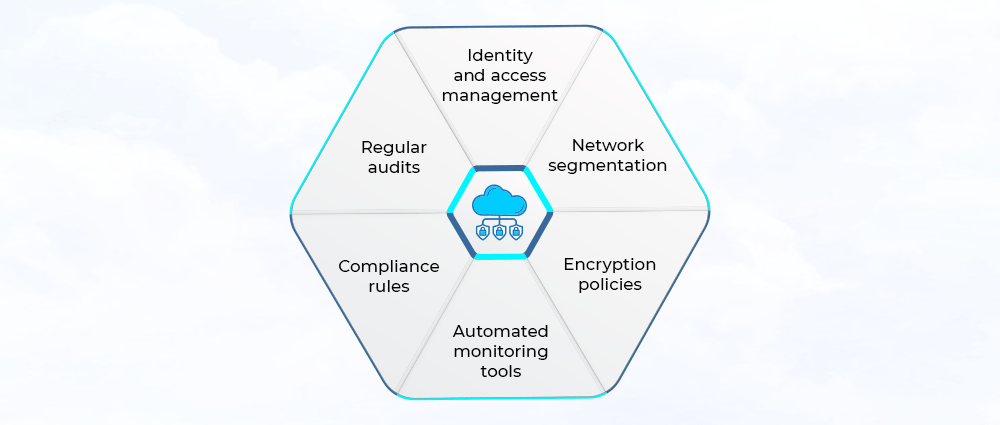
Imagine cloud security architecture as the plan of your digital structure. It determines the protection of the whole entity from top to bottom.
A robust structure consists of:
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
This establishes who has access to which resource. IAM is the tool in cloud security that guarantees that the authorized people at the right time have access only to the right systems. Role-based permissions, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and thorough identity verification are used to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Network segmentation
The media of the network are organized in such a way that the critical systems are separated from the ordinary ones. Network segmentation contributes to the reduction in the size of the network and makes it easier to control while at the same time confining the attacker to a smaller area, provided that they break in.
Therefore, only a minor part of the cloud environment is exposed to the attack and the rest remains untouched.
3. Encryption policies Data
It is kept in such a way that even if the attacker has access, they cannot read it. The practice of making information un-readable or non-readable by employing mathematical techniques is called encryption and enabling security information in all data that is to be protected by the company.
Encryption takes place not only when the data is in the process of being transmitted but also when it is stored. Therefore, even if the data gets intercepted, it will still be gibberish to the person without the key.
4. Automated monitoring tools
These are like security personnel that are always watching and can immediately report any dubious activities. They continually alert your staff whenever there is some unusual activity occurring like an unauthorized login, large data transfer, changing the system configuration, etc.
Hence, you will be in a position to neutralize the threats before they escalate into a major incident.
5. Compliance rules
Refrain from risking situations that may lead to violations of GDPR, HIPAA, ISO, PCI DSS, and other regulations.
The path of compliance has its advantages and among them is the fact that it helps to streamline the data-processing which in turn leaves no room for legal complications and makes customers trust you.
6. Regular audits
These are the means that help you reveal the loopholes which, if unaddressed, maybe exploited by attackers.
During auditing, you can review existing settings, permissions, etc. So, a good cloud security architecture reduces risk and ensures long-term safety.
Enterprise Cloud Security Trends for 2026
Big corporations are investing in cloud services not only to just store their data, but also for protection. The following are the main trends that will impact enterprise cloud security in 2026:
1. Zero Trust Access Models
“Trust no one, verify everything.”
The principle ensures that every user and every request is still checked before being allowed in, regardless of whether they are inside the network. It makes it extremely difficult for the intruders to take advantage of the situation and traverse laterally once they succeed penetrating one area of the system.
2. AI-driven threat detection
AI tools spot abnormal activities in no time at all.
Modern AI has the capacity to map out what a “normal” usage pattern looks like and instantly flag any activity as suspicious. Hence, the reaction time is minimized and the threat is eliminated right at the beginning.
3. Automated CSPM
Instantly tells and corrects misconfigurations.
CSPM instruments continuously monitoring the cloud environments for the weakest security settings and the auto-correction of those settings take place. This practice of no human intervention removes the error of human being and at the same time keeps your cloud secure whilst expanding.
4. Multi-cloud visibility dashboards
A single interface for the control of AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and local servers.
This provides security teams an overall view of their landscape. When everything is centralized, then it is much easier to not only see potential threats but also to control security measures across different systems.
5. Security embedded into development pipelines
Security verification is performed during development and implementation automatically.
With this, the risks associated with delayed detection of app vulnerabilities get reduced significantly since the app is still in development stage. Plus, it takes less time, lowers the risk and keeps the software protected from the first line of code.
Small organizations are able to implement the simplified versions of these practices as well.
How Companies Should Start Strengthening Their Cloud
Many organizations realized that there was a need for better cloud security, however, they were not sure where to start. The most effective way is to take a small step and then a gradual increase afterward. The following is a simple roadmap:
1. Map your complete cloud environment
Get to know what you have and where it is. This will help you to prevent blind spots and also ensure that every application and service is included. It is not possible to protect assets effectively without complete visibility.
2. Point out your sensitive data and critical workloads
Your most important assets deserve the highest level of protection. This comprises customer data, financial records, or proprietary systems. Once these are unambiguously identified, you are able to determine your security efforts in the right order.
3. User permissions review
Adhere to the least privilege rule. Users should be given the minimum access rights necessary for them to perform their jobs. This will greatly lower the risk of both accidental and deliberate misuse.
4. Suppress unnecessary or obsolete access rights
The presence of ex-employees and inactive accounts brings a considerable amount of risk. Even if the access has not been revoked, it could still be easily abused. Periodic clean-up will ensure that only those with proper authorization will access your cloud resources.
5. Monitor for suspicious activities
Receive notifications for unexpected downloads, logins, or changes. This will allow your team to react promptly to the attack signs. The real-time monitoring is very helpful in not letting small issues that escalate into big ones.
6. Employee training
Most cloud breaches can be traced back to human errors. Employees should be trained on how to identify phishing attempts, create strong passwords, and follow secure methods. A well-done training program turns your staff into the strongest line of defense.
7. When possible, automate
Automation brings down errors and speed up the process. Security tools that are automated can identify threats, impose rules, and rectify misunderstandings.
Cloud-Native Security Practices
Applications that are cloud-native necessitate corresponding security measures in the cloud. The classic measures do not perform well in the environment of containers, microservices, and Kubernetes. The main cloud-native security practices are:
1. Embed security into development
Shift security left that is, start during coding and not after deployment. This enables the discovery of vulnerabilities earlier resulting in saving time and consequently reducing risks. Besides, it will be the case that security is now a part of your culture and not merely an afterthought.
2. Scan container images
Make certain that they are clean before sending them to production. The scanning process assists in identifying old libraries or harmful components. This also ensures that your workloads are shielded from the threats hidden inside container images.
3. Detect vulnerabilities in real-time
Today’s systems must have instantaneous responsiveness. The real-time detection tools will notify you at the very moment when anything suspicious happens. This proactive method significantly restricts the extent of the harm done before the assailants can go further into your system.
4. Manage secrets safely
It is very unwise to keep your passwords or API keys in the code. The use of secret managers or vaults is the best way to keep your credentials safe. The practice of proper secret management greatly reduces the risk of accidental exposure or credential theft.
5. Protect workloads at runtime
Deploy real-time monitoring tools that discern unusual behavior. Protection at runtime enables the capture of threats that have managed to avoid being screened earlier. It guarantees that your applications remain secure even in the course of an attack being executed.
Cloud-native security is not only faster but also smarter and more adaptable compared to the older systems.
Protecting Data Where It Lives: Cloud Storage Security Tips
Cloud storage is a favorite target for cybercriminals. One misconfiguration could expose your entire database.
Here’s how to secure it:
- Make all storage buckets private by default
- Encrypt data at rest and during transit
- Limit access to only those who need it
- Monitor for unusual or large downloads
- Review settings regularly
- Use automated alerts for suspicious activity
These tips reduce the risk of accidental exposure or intentional attacks.
Cloud Computing Security Tips for Remote Workplaces
Remote work isn’t going away. Teams now access cloud systems from offices, homes, cafés, airports, anywhere. This creates more entry points for attackers.
To stay secure:
- Enforce secure logins: Do not allow login from unknown or unsafe networks.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA): Adds a second layer of verification.
- Monitor device health: Ensure devices aren’t infected or outdated.
- Block unsafe Wi-Fi connections: Public networks are dangerous.
- Remove access when employees leave: Offboarding must be immediate.
- Use cloud network security tools: Virtual firewalls, VPNs, and endpoint protection help a lot.
Remote work is convenient, but only if protected properly.
Tips for Choosing AI Solutions for Cloud Security
AI is becoming a crucial part of cloud security. It helps detect threats, block attacks, and respond automatically.
When choosing AI-powered tools, look for:
- High accuracy
- Low false alerts
- Real-time threat detection
- Easy integration with your cloud platform
- Automated incident response
- Clear explanations of alerts
- Scalability as your workloads grow
AI should make your security easier, not more complicated.
Tips for Picking the Right AI Security Tools
Before selecting an AI security vendor, evaluate:
- Their reputation
- Quality of their training data
- Ability to analyze cloud network security logs
- Support for multi-cloud and hybrid setups
- Cost and flexibility
- Dashboard and reporting clarity
These factors help you choose tools that actually deliver results.
Top Tips for Picking the Right Cloud Security Tools
There are hundreds of cloud security tools, but not every tool fits every business. The best tool is the one that meets your specific needs.
When choosing cloud security tools, consider:
- Your cloud platform (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Built-in features you already have
- The visibility you need
- Identity and access management needs
- Compliance requirements
- Threat detection accuracy
- Existing system compatibility
- Pricing and ease of use
A good tool shouldn’t add complexity, it should remove it.
Tips for Picking a CNAPP in Cloud Security
A CNAPP (Cloud Native Application Protection Platform) combines multiple security functions into one tool:
- Vulnerability scanning
- CSPM (Security posture management)
- Compliance monitoring
- Runtime protection
- Infrastructure scanning
- Identity risk analysis
When selecting a CNAPP, look for:
- Automated remediation
- Multi-cloud support
- Accurate risk prioritization
- Real-time dashboards
- Strong API integrations
A CNAPP simplifies cloud security by giving you everything in one place.
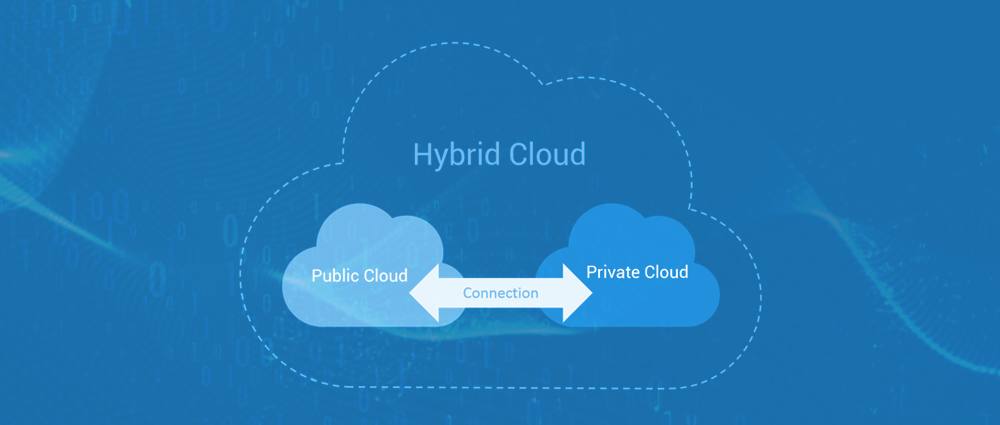
Hybrid Cloud Security Tips
A hybrid cloud combines public cloud, private cloud, and on-premise systems. Securing all these environments at once is challenging.
Keep this above headings, replace the below with image:
Here’s what helps:
The key to hybrid cloud security is visibility, you must see everything happening everywhere.
Building a Cloud Security Culture
Technology alone won’t protect your business. People matter just as much. A strong cloud security culture reduces mistakes and prevents breaches.
You can build this culture by:
- Training teams regularly
- Teaching employees to identify phishing
- Encouraging strong passwords
- Educating teams on cloud risks
- Sharing best practices internally
- Creating simple reporting channels
Most security failures come from human error, train your team well, and you cut risk dramatically.
Improving Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Your cloud environment changes constantly. New apps get added, new users join, policies evolve. That’s why CSPM is crucial.
To improve your posture:
- Use automated scanning
- Fix misconfigurations immediately
- Monitor compliance continuously
- Track all user activity
- Set up real-time alerts
- Review system changes regularly
A strong CSPM keeps your cloud environment aligned with industry best practices.
The Future of Cloud Infrastructure Security
As we move beyond 2026, cloud security will continue to evolve. Expect to see:
- Predictive AI that blocks threats before they happen
- Automated policy enforcement
- Stronger zero trust frameworks
- New encryption innovations
- Advanced CNAPP capabilities
- Full visibility across multi-cloud and hybrid systems
Companies that invest in cloud security today will be far more resilient tomorrow.
Final Thoughts
The future of cloud security in 2026 is a promise of better, modern, and a well-planned method. The vulnerabilities are made more intelligent but the tools and techniques to combat them are also being developed along with that. Your trust with the customers will remain unbroken when you cut your risks down, that is, by simply following the 27 tips related to cloud security mentioned in this guide.
An environment of the cloud that is secure cannot be claimed solely with the use of tools but rather through awareness, consistency, and continuous improvement. Amsat can help you here by offering the whole range of cloud security services starting from threat detection to CSPM implementation, IAM optimization, compliance support, and monitoring 24/7. Amsat not only assures that your infrastructure is protected, managed, and waiting for the future, whether you operate a multi-cloud environment or a cloud-native one that is scaling.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the best practices for cloud security?
They would be basically identity management, encryption, employee training, multi-factor authentication, cloud security posture management, regularly performed audits, and strong cloud-native security practices.
2. What are the 7 pillars of cloud security?
The seven pillars of cloud security are:
- Identity control
- Data protection
- Network security
- Application security
- Monitoring and alerting
- Compliance
- Security
3. Which tool is commonly used in cloud security?
The tools widely used in the area are CNAPPs, SIEM Security Information and Event Management tools, cloud firewalls, identity management systems, CSPM tools, and threat detection platforms.
4. What are the 5 main security threats on the cloud?
The main risks are misconfigurations, unauthorized access, data breaches, insecure APIs, and insider threats.
TAGS
- Cyber Security
- Penetration Testing