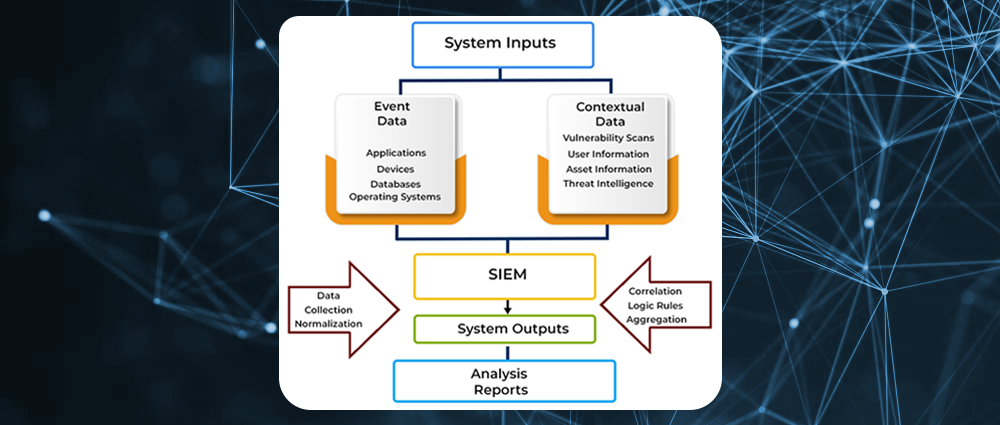
Security information and event management (SIEM) is a security management approach that combines security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM) functions into a single system. SIEM platforms collect log and event data from security systems, networks, and computers, and convert it into actionable security insights.
A security management system that can help organizations improve their security posture in a number of ways, SIEM can spot threats that individual security systems cannot see, examine past security incidents, perform incident response, and prepare reports for regulation and compliance purposes. Also, security information and event management (SIEM) open-source tools can provide organizations with a cost-effective way to improve their security posture.
SIEM systems typically work by collecting and aggregating event data from multiple sources, such as firewalls, servers, applications, and network devices. They also detect aberrations from the norm, such as uncommon spikes in traffic, botched login attempts, or suspicious activity. In addition, they take appropriate action, such as generating alerts, blocking traffic, or isolating infected devices.

While SIEM systems can be deployed in many different ways, there are two common architectures, including:
Traditional SIEM platforms: These platforms gather and store log data in a centralized location or data store. Traditional SIEM platforms are typically designed to handle large volumes of data, but they can be complex and expensive to implement and maintain.
Modern SIEM architecture based on data lake technology: These platforms use a data lake to store raw data in its original format, making it easier to evaluate and correlate data from multiple sources. However, managing and securing it can also be an uphill task.
Irrespective of the architecture, SIEM systems play a vital role in helping organizations improve their security posture. Provision of real-time analysis of log and event data can also enable SIEM systems to help organizations identify threats and respond to incidents quickly and effectively.
Data Collection
SIEMs collect logs and events from hundreds of organizational systems. Each device generates an event every time something happens, and collects the events into a flat log file or database. The SIEM can collect data in four ways:
- Via an agent installed on the device (the most common method)
- By directly connecting to the device using a network protocol or API call
- By accessing log files directly from storage, typically in Syslog format
- Via an event streaming protocol like SNMP, Netflow or IPFIX
The SIEM is tasked with collecting data from the devices, standardizing it and saving it in a format that enables analysis.
SIEM Architecture
SIEM architecture is typically divided into three layers:
-
Data collection layer: This layer is responsible for collecting security data from a variety of sources, such as firewalls, servers, applications, and network devices. Data can be collected in real time or in batches.
-
Data aggregation and analysis layer: This layer is responsible for aggregating and analyzing the collected data to identify potential security threats. SIEM systems use a variety of techniques to analyze data, including correlation, rule-based detection, and machine learning.
-
Reporting and alerting layer: This layer is responsible for generating reports and alerts based on the findings of the data analysis layer. Reports can be used to track security trends and to identify areas where security posture can be improved. Alerts can be used to notify security personnel of potential security threats so that they can take action quickly.
Simply put, SIEM systems collect data from a variety of sources, analyze it for potential threats, and generate reports and alerts.
The three layers of SIEM architecture work together to provide a comprehensive security monitoring and management solution.
Operational Best Practices for SIEM
Operational best practices for SIEM are recommendations for how to use a SIEM system effectively and efficiently. These best practices can help organizations to get the most out of their SIEM investment and to improve their overall security posture.
Some common operational best practices for SIEM include:
- Define clear objectives: What do you want to achieve with your SIEM system? Do you want to detect specific threats? Investigate incidents more quickly? Improve compliance? Once you know your objectives, you can tailor your SIEM configuration and operations to achieve them.
- Collect the right data: SIEM systems can collect data from a wide variety of sources. However, it’s important to only collect the data that is relevant to your objectives and that you can realistically analyze. Collecting too much data can make it difficult to find the signal in the noise.
- Use correlation and analytics: SIEM systems are most powerful when they are used to correlate data from different sources and to apply analytics to identify patterns and trends. This can help you to detect threats that would be difficult to find if you were only looking at data from individual sources.
- Tune your alerts: SIEM systems can generate a lot of alerts, so it’s important to tune them so that you are only notified of the most important events. This will help you to avoid alert fatigue and to focus on the threats that matter most.
- Monitor your SIEM system: It’s important to monitor your SIEM system regularly to ensure that it is performing properly and that you are not missing any important alerts. You should also review your SIEM configuration regularly to make sure that it is still aligned with your objectives.
In addition to these general best practices, there are a number of specific best practices that organizations can follow to improve their SIEM operations. For example, organizations can:
- Develop a SIEM incident response plan: This plan should outline the steps that will be taken to investigate and respond to security incidents detected by the SIEM system.
- Integrate the SIEM system with other security tools: This can help to streamline security operations and to improve the efficiency of incident response.
- Provide SIEM training to security personnel: It’s important to ensure that security personnel know how to use the SIEM system effectively. This will help them to get the most out of the system and to identify and respond to threats more quickly.

Modern SIEM Solutions
Modern SIEM solutions are increasingly cloud-based and offer a variety of advanced features, including:
- Machine learning: Modern SIEM solutions use machine learning to identify patterns and anomalies in security data. This can help to detect threats that would be difficult to identify using rule-based detection alone. For example, a machine learning algorithm might be able to detect a new type of malware that has not yet been identified by security researchers.
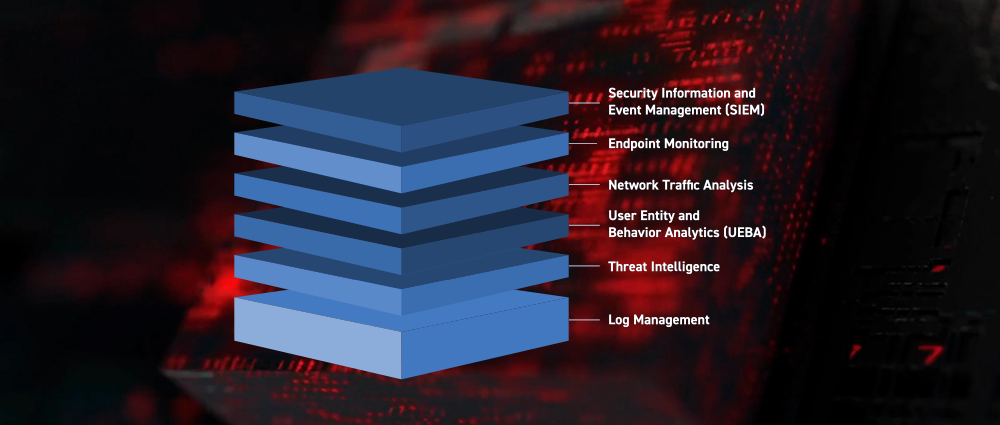
- User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA): UEBA is a type of machine learning that analyzes user and entity behavior to identify anomalous activity. This can be helpful for detecting insider threats and other types of attacks that are difficult to detect using traditional methods. For example, a UEBA algorithm might be able to detect a user who is logging in from an unusual location or time.
- Threat intelligence integration: Modern SIEM solutions can integrate with threat intelligence feeds to get the latest information about known threats. This information can be used to improve the accuracy of SIEM alerts and to identify new threats as they emerge. For example, a SIEM solution might be able to use threat intelligence to identify a new IP address that is known to be associated with a phishing campaign.

These advanced features can help organizations to improve their security posture by detecting threats more quickly and accurately. In fact, modern SIEM solutions are more powerful and easier to use than ever before. They can help organizations to detect threats more quickly and accurately, and to improve their overall security posture.
Benefits of SIEM
SIEM systems can provide a number of benefits to organizations, including:
- Improved security posture: SIEM systems can help organizations to improve their security posture by detecting and responding to security threats more quickly and effectively.
- Reduced risk of data breaches: SIEM systems can help organizations to reduce the risk of data breaches by detecting malicious activity early on.
- Improved compliance: SIEM systems can help organizations to comply with industry regulations and standards by providing a central repository for security data and by generating reports that can be used to demonstrate compliance.
Next-gen SIEM
Next-generation SIEM (security information and event management) systems go beyond traditional SIEM capabilities by using machine learning and behavioral profiling to detect anomalies and trends in security data. This allows them to identify threats that would be difficult or impossible to detect using traditional rule-based methods.
Next-generation SIEM systems also typically have the ability to retain and analyze large volumes of historical data. This enables them to detect threats that may have been present in the data for some time, but were not previously identified.
One of the key benefits of next-generation SIEM systems is their ability to perform deep behavioral analysis. This involves analyzing user and entity behavior over time to identify patterns and anomalies. For example, a next-generation SIEM system might be able to detect an employee who is logging in from unusual locations or times, or who is accessing files that they are not authorized to access.
Next-generation SIEM systems are more powerful and versatile than traditional SIEM systems. They can help organizations to detect threats more quickly and accurately, and to improve their overall security posture.
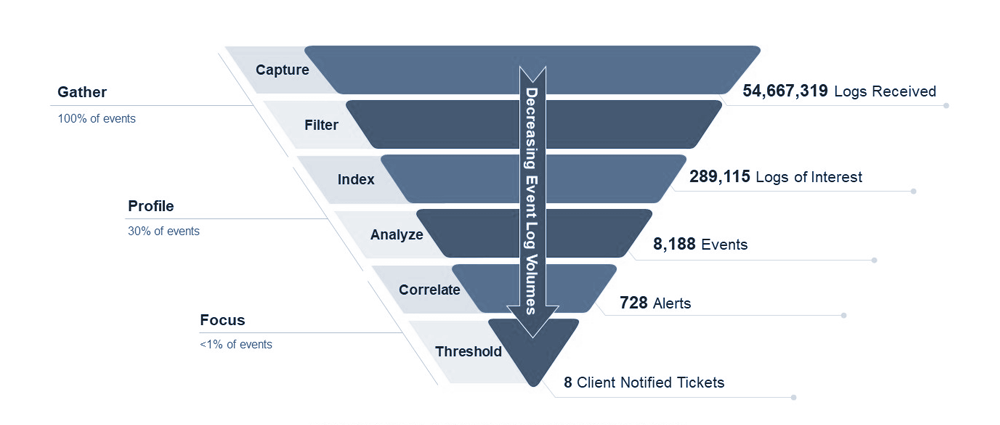
The Log Flow
SIEM systems collect 100% of log data from across an organization, but only a small fraction of that data is relevant for security purposes. SIEM systems use a variety of techniques to filter out noise and identify the most relevant data, including:
Log filtering: SIEM systems can filter out noise from logs by using rules to remove data that is not relevant for security purposes. For example, a SIEM system might be configured to filter out logs from known trusted IP addresses.
Log aggregation: SIEM systems aggregate logs from different sources into a single view. This makes it easier to identify patterns and trends in the data.
Log analysis: SIEM systems use a variety of techniques to analyze logs for security threats. These techniques include correlation, rule-based detection, and machine learning.
Once a SIEM system has identified the most relevant data, it can generate security alerts. Security alerts are notifications that are sent to security personnel to let them know about potential security threats.
SIEM platforms can integrate with a variety of security and organizational data sources, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems, antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) software, network devices, servers, applications, cloud platforms, and business systems.
Which SIEM Hosting Model Should You Go for?
The best SIEM hosting model for you will depend on your specific needs and requirements. Here are some considerations to help you make a decision:
Existing SIEM infrastructure: If you already have a SIEM infrastructure in place, you may want to consider self-hosting or leveraging a managed security service provider (MSSP) to help you manage your SIEM.
Data off-premises: If you are able to move data off-premises, a cloud-hosted or fully managed SIEM model can reduce costs and management overhead.
SIEM expertise: If you do not have security staff with SIEM expertise, you may want to consider a hybrid-managed or SIEM-as-a-Service model.
Hardware Sizing
To size hardware for your SIEM, consider the following factors after determining your event velocity and volume:
Storage format: How will files be stored? Flat file format, relational database, or unstructured data store like Hadoop?
Storage deployment and hardware: Can data be moved to the cloud? If so, cloud services like Amazon S3 and Azure Blob Storage are attractive for storing most SIEM data. If not, consider local storage resources, and whether to use commodity storage with Hadoop or NoSQL DBs, or high-performance storage appliances.
Log compression: What technology is available to compress log data? Many SIEM vendors advertise compression ratios of 1:8 or more.
Encryption: Is there a need to encrypt data as it enters the SIEM data store? Determine software and hardware requirements.
Hot storage (short-term data): Needs high performance to enable real-time monitoring and analysis.
Long-term storage (data retention): Needs high-volume, low-cost storage media to enable maximum retention of historic data.
Failover and backup: As a mission-critical system, the SIEM should be built with redundancy, and be backed with a clear business continuity plan.
Scalability and Data Lakes
Modern networks are large and complex, and they generate a huge amount of data. SIEM technology is used to make sense of this data and identify security threats. However, SIEMs can be expensive and unable to store all of the data that is generated.
Data lakes offer a solution to these problems. They can store large volumes of data at a low cost, and they can be used to process data using big data tools like Hive and Spark. This makes data lakes ideal for storing and analyzing SIEM data.
Benefits of Using a Data Lake with SIEM
Nearly unlimited, low-cost storage: Data lakes can store large volumes of data at a low cost because they use commodity hardware. This is in contrast to traditional SIEMs, which can be expensive to scale.
New ways of processing big data: Data lakes can be used to process data using big data tools like Hive and Spark. These tools are designed to handle large volumes of data quickly and efficiently.
The possibility of retaining all data across a multitude of new data sources: Data lakes can store data from a variety of sources, including cloud applications, IoT devices, and mobile devices. This makes it possible to retain all of the data that is generated by an organization, even if it comes from new and emerging sources.

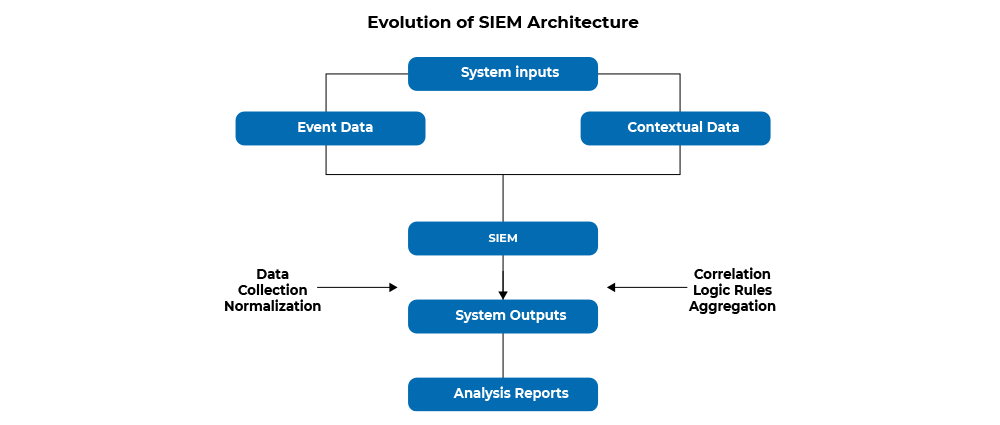
Evolution of SIEM Architecture
SIEMs have evolved from expensive, monolithic infrastructures to more agile, lightweight, and intelligent solutions. Next-generation SIEMs offer the following benefits:
Modern data lake technology: SIEMs can now leverage big data storage to provide unlimited scalability, low cost, and improved performance.
Managed hosting and management options: Managed security service providers (MSSPs) can help organizations implement and manage SIEMs, either on-premises or in the cloud.
Dynamic scalability and predictable costs: SIEM storage can now grow dynamically and predictably as data volumes increase, eliminating the need for meticulous sizing and architectural changes.
Data enrichment: Modern SIEMs can enrich data with context to filter out false positives and improve the detection and response to real threats.
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): SIEMs now include advanced analytics components such as machine learning and behavioral profiling to discover new relationships and anomalies across huge data sets.
Security Orchestration and Automation (SOAR): Modern SIEMs can leverage SOAR technology to identify and automatically respond to security incidents, and support incident investigation by security operations center (SOC) staff.
Conclusion
A cyber-security technique that focuses on the security of IT networks, SIEM safeguards the entire IT infrastructure by keeping a close watch and analyzing the resources within IT networks.
SIEM architecture components—which include log management, data collection, and analysis—provide a slew of benefits for businesses of all sizes, from compliance reporting to foiling attacks. SIEM architecture components include log management, data collection, correlation, and analysis. To effectively manage SIEM alerts, it is crucial to avoid alert fatigue and ensure the security operations team can prioritize security alerts.
Security information and event management (SIEM) implementation is a critical step in improving any organization’s security posture. By following these best practices, organizations can improve their overall security posture and detect incidents that may have gone unnoticed.